Atropine
It is quite difficult to give a precise definition for the class of compounds referred to as alkaloids [1]. However it is probably fair to say that the definition proposed by Ladenburg in the late 1880s is probably reasonable and still valid today. Ladenburg suggested that alkaloids were compounds:
-
derived from plants
-
with a basic character (hence the term alkaloid from alkali)
-
contained a nitrogen based heterocylic ring within their molecules
In general alkaloids are physiologically very active and often extremely poisonous - they are the "bad guys" of the natural products world. Having said this, many find applications in medicine when administered in small doses.
Alkaloids can be sub-categorised [2] according to:
-
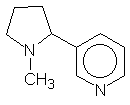
Monocyclic alkaloids - which contain only one ring. A typical monocyclic alkaloid is nicotine:
-
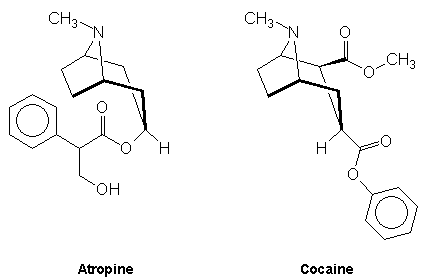
Bicyclic alkaloids - these may be illustrated by the tropane alkaloids which consist of molecules with a 1,4 nitrogen bridged cycloheptane structure. Atropine and cocaine are examples
-
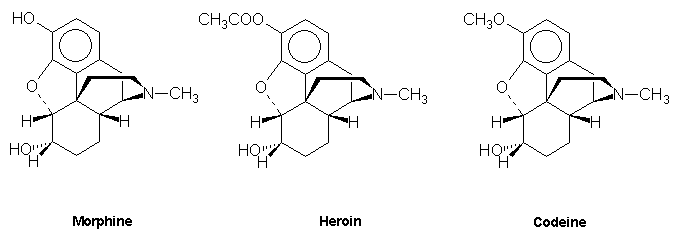
Polycyclic alkaloids such as strychnine, lysergic acid, cannabinol, morphine, heroin and codeine.