EndosulfanThe controversial insecticide
Paul May
Also available: HTML, JMol, and VRML versions.
|
EndosulfanThe controversial insecticide
Paul May
Also available: HTML, JMol, and VRML versions.
|
Endosulfan is an insecticide which was first introduced in the 1950s, and is commonly knoiwn by its trade-name Thiodan. It is classed as an organochlorine, which are molecules notorious for being persistent organic pollutants (POPs). The problem with POPS is that they hang around a long time after use, which means they build up to high concentrations in the environment, at which levels they may become toxic to plants and animals. There is now a call for a worldwide ban on POPs because of their possible links to cancer and effects on hormones, the immune system, and reproduction. However, unlike other POPS which disperse across the world, endosulfan tends to remain close to its region of use. Nevertheless, it has been found in high concentrations in many areas around the world because it is so widely used.
Endosulfan is produced by the Diels-Alder reaction of hexachlorocyclopentadiene with cis-butene-1,4-diol. The product is then reacted with thionyl chloride, liberating HCl.
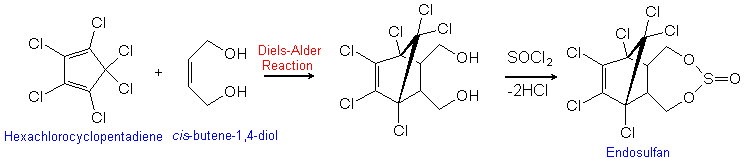
Endosulfan is actually a mixture of stereoisomers, designated α and β. α-Endosulfan is the more thermodynamically stable, thus at room temperature β-endosulfan slowly converts irreversibly to the α-form.
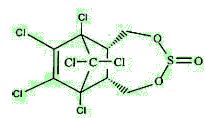
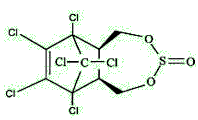
α-endosulfan. β-endosulfan.
Endosulfan has 2 modes of action, each associated with different parts of the molecule. The chlorinated parts alter the electrophysiological and enzymatic properties of nerve cell membranes, causing a change in the kinetics of Na+ and K+ ion flow through the membrane. Disturbances of calcium transport of Ca+2-ATPase activity may also be involved, as well as phosphokinase activities (Hayes and Laws, 1991). At the same time, the cyclodiene part hinders the action of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which induces the uptake of chloride ions by neurons. The blockage of this activity results in only partial repolarization of the neuron, leaving it in a state of uncontrolled excitation (Klassen and Watkins, 1999).
It's used in agriculture worldwide to control insect pests, including whiteflies, aphids, leafhoppers, Colorado potato beetles and cabbage worms. It also kills many types of mites, ticks and also tstetse flies. Because of its unique mode of action, it is useful in contolling insects that have become resistant to other forms of insecticide. However, its major drawback is that it is non-specific, it kills all insects whether they are harmful (such as those in the list above) or beneficial (such as honeybees!). It is used extensively in India and the US in crops such as cotton, potatoes, tomatoes, and apples, but its use in the US is gradually being phased out.
 |
 |
Above: Colorado potato beetle. |
Above: Aphid. |
 |
 |
 Although it's an extremely effective insecticice, endosulfan is one of the most toxic pesticides on the market today. It is believed to be responsible for many fatal pesticide poisoning incidents around the world (Pan Magazine, 2006). Endosulfan is also a synthetic substance that imitates or enhances the effect of the female hormone estrogen, which means it can cause reproductive and developmental damage in both animals and humans. Researchers studying children from an isolated village in Kerala, India have linked endosulfan exposure to delays in sexual maturity among boys (Saiyed et al, 2003). In the study, endosulfan was the only pesticide applied to cashew plantations in the hills above the village for 20 years, and was found to have contaminated the environment around the village. The researchers compared these villagers to a control group of boys from a demographically similar village that lacked a history of endosulfan pollution. The exposed boys had high levels of endosulfan in their bodies, relative to the control group, plus lower levels of the male hormone testosterone. The exposed boys also exhibited delays in reaching sexual maturity. Birth defects of the male reproductive system were also more prevalent in the study group.
Although it's an extremely effective insecticice, endosulfan is one of the most toxic pesticides on the market today. It is believed to be responsible for many fatal pesticide poisoning incidents around the world (Pan Magazine, 2006). Endosulfan is also a synthetic substance that imitates or enhances the effect of the female hormone estrogen, which means it can cause reproductive and developmental damage in both animals and humans. Researchers studying children from an isolated village in Kerala, India have linked endosulfan exposure to delays in sexual maturity among boys (Saiyed et al, 2003). In the study, endosulfan was the only pesticide applied to cashew plantations in the hills above the village for 20 years, and was found to have contaminated the environment around the village. The researchers compared these villagers to a control group of boys from a demographically similar village that lacked a history of endosulfan pollution. The exposed boys had high levels of endosulfan in their bodies, relative to the control group, plus lower levels of the male hormone testosterone. The exposed boys also exhibited delays in reaching sexual maturity. Birth defects of the male reproductive system were also more prevalent in the study group.
 Endosulfan is an acute neurotoxin to both insects and mammals, including humans. The US Environmental Protection Agency classifies it as Category I: "Highly Acutely Toxic" (EPA 2002) while the World Health Organization classifies it as Class II "Moderately Hazardous" (WHO, 2005). Symptoms of acute poisoning include hyperactivity, tremors, convulsions, lack of coordination, staggering, difficulty breathing, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, and in severe cases, unconsciousness (ATSDR, 2000). Doses as low as 35 mg/kg have been documented to cause death in humans, and many cases of poisoning have resulted in permanent brain damage. Farm workers with chronic endosulfan exposure are at risk of rashes and skin irritation.
Endosulfan is an acute neurotoxin to both insects and mammals, including humans. The US Environmental Protection Agency classifies it as Category I: "Highly Acutely Toxic" (EPA 2002) while the World Health Organization classifies it as Class II "Moderately Hazardous" (WHO, 2005). Symptoms of acute poisoning include hyperactivity, tremors, convulsions, lack of coordination, staggering, difficulty breathing, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, and in severe cases, unconsciousness (ATSDR, 2000). Doses as low as 35 mg/kg have been documented to cause death in humans, and many cases of poisoning have resulted in permanent brain damage. Farm workers with chronic endosulfan exposure are at risk of rashes and skin irritation.
As a result of its poisonous and persistent nature, endosulfan has been banned from many developed countries, and is gradually being phased out in most of the rest (see poster, right). It is already banned in Australia, New Zealand, Belize, Singapore, Bangladesh, Indonesia, Korea, Thailand but still in use in India, Taiwan and the US and some EU countries (although its use is severely restricted) such as Denmark and Great Britain. In 2010 the Stockholm Convention's Persistent Organic Pollutants Review Committee (POPRC) nominated endosulfan to be added to the Stockholm Convention in April 2011, which should finally result in a global ban (POPRC 2010).
![]()