Site Designer:
Claire Rosling
Email:
Site Designer:
Claire Rosling
Email:
Introduction
Serotonin was first recognised as a powerful vasoconstrictor in blood serum. It was isolated in 1948 by Page and was later found to be associated with the central nervous system.
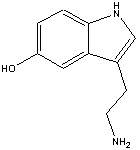 The
chemical name for serotonin is 5-hydoxytryptamine which is often abbreviated to
5-HT.
The
chemical name for serotonin is 5-hydoxytryptamine which is often abbreviated to
5-HT.
Serotonin is naturally produced in the Pineal gland which lies deep at the centre of the human brain. The average adult human possesses only 5 to 10 mg of serotonin, 90 % of which is in the intestine and the rest in blood platelets and the brain.
One role of this 'wonder drug' is as a neurotransmitter, allowing numerous functions in the human body including the control of appetite, sleep, memory and learning, temperature regulation, mood, behaviour, cardiovascular function, muscle contraction, endocrine regulation and depression. Subsequent to his discovery of Serotonin, Page commented that no physiological substance known possesses such diverse actions in the body as does serotonin.
5-HT is also found in wasp stings and scorpion venom where its function is of an irritant, since intravenous injection of serotonin in humans leads to pain, gasping, coughing, a tingling and prickling sensation, nausea, cramps and other unpleasant symptoms.
