Examples of p electron charge and p electron bond
order calculations
Ethene
1 (doubly) occupied
MO: y1 = 1/Ö2 (f1 +f2)
p electron charge on atom 1 = q1=
2((1/Ö2)2
= 1
p bond order between atoms 1 and 2 = p12 = 2((1Ö2)(1Ö2)) = 1
(i.e. p bond order for double bond = 1)
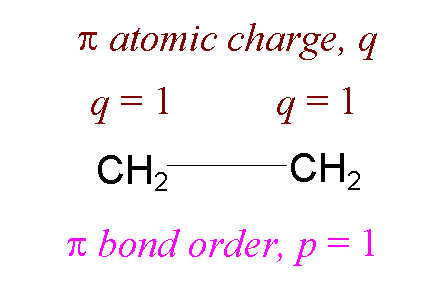
1, 3-Butadiene
2 occupied MOs (both doubly occupied),
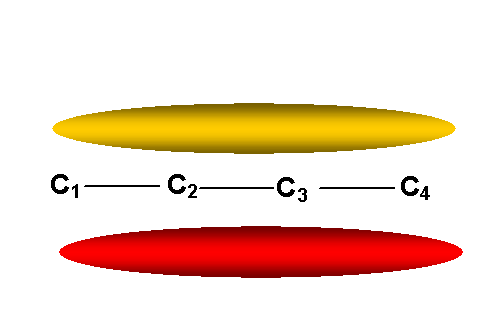
y1 = 0.37f1 + 0.60f2 + 0.60f3 + 0.37 f4 E= a + 1.62b
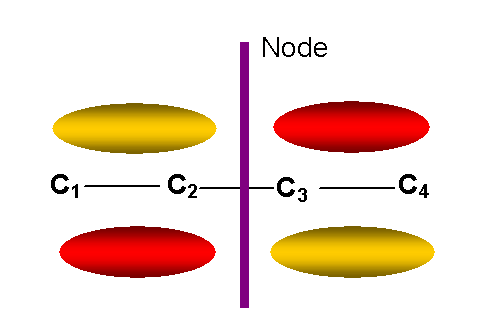
y2 = 0.60f1 + 0.37f2 – 0.37f3 – 0.60f4 E= a + 0.62b
p electron charge
on atom 1 = q1 = 2 (0.372
+ 0.602) @ 1
p electron charge on atom 2 = q2 = 2 (0.602 +
0.372) @ 1
Similarly, q3
= , q4 = 1
p electron bond
order between atoms 1 and 2 = p12
= 2 ((0.37 x 0.60) + (0.60 x 0.37)) = 0.89 (similarly, p34=0.89)
p electron bond
order between atoms 1 and 2 = p12
= 2 ((0.37 x –0.37) + (0.60 x 0.60)) = 0.45
Summary: for 1,3-butadiene we obtain:
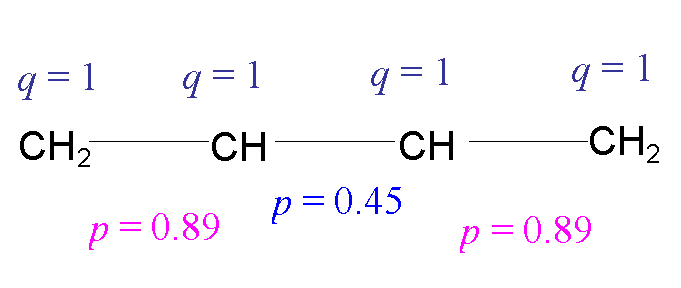
So according to Hückel theory, the central
bond in 1,3-butadiene has less double bond character than the outer bonds,
as in a simple drawing