The Chemistry of Sorbic Acid
Sorbic acid is a white crystalline solid. It has a melting point of 134.5°C, a boiling point of 228°C and a pKa of 4.76.
The chemistry of sorbic acid is determined by the carboxyl group and the conjugate double bonds:
Conjugated Double Bonds
Sorbic acid is brominated faster than other olefinic acids
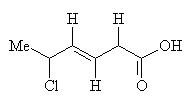
Reaction with HCl predominately gives 5-chloro-3-hexenoic acid:

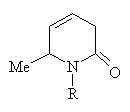
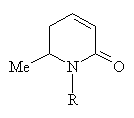
Reactions with amines at high temperatures under pressure lead to mixtures of dehydro-2-piperidines:
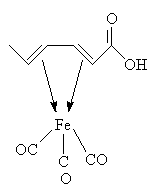
A yellow crystalline complex melting at 198°C is formed from sorbic acid and iron tricarbonyl:
Sorbic acid is oxidised rapidly in the presence of molecular oxygen and peroxide compounds. Decomposition products indicate that the double bond furthest from the carboxyl group is oxidised.
It takes part in Diels-Alder reactions with many dienophiles and undergoes self-dimerisation. Dimerisation leads to eight possible isomeric Diels-Alders structures.
Carboxylic Acid Group
Sorbic acid undergoes the normal acid reactions forming salts, esters, amides and acid chlorides.