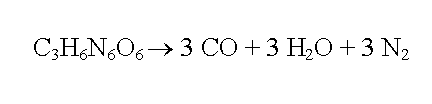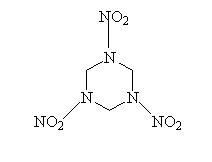
RDX
Structure

Properties
Appearance White solid
Molecular weight 222.1
Melting Temperature 204° C, high but lowers when mixed with TNT
Thermal ignition temp 260° C
Stability High chemical stability, especially compared to TNT
Solubility Difficult to dissolve in organic liquids
Sensitivity Easily initiated by impact of friction, often coated with oil or wax
History
1899 RDX first prepared by a German named Henning for use in medicine.
1920 RDX first recognised as a possible explosive.
1940 A continuous method for the preparation of RDX was developed.
RDX was used with TNT to fill bombs and shells during the Second World War by both sides in order to create more powerful weapons.
Manufacture
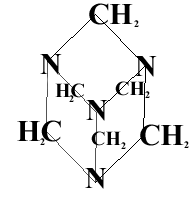
Th best way to make RDX is to use the compound pictured above and react it with ammonium nitrate and concentrated nitric acid. The mixture is warmed and when cold water is added, RDX is precipitated. The mechanism for this reaction is very complicated.
Decompostition Products
RDX, like TNT, does not have enough oxygen in its molecular formula to completely oxidise everything during an explosion. It is only after contact with the atmospheric oxygen that can allow complete combustion to occur. Below is the decomposition reaction of RDX.