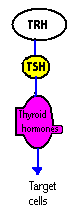
 TSH is the major regulator of the thyroid
gland, it is a glycoprotein hormone which binds with receptors at the surface of
the thyroid follicular cell, this stimulates the release of T3 and T4
from the thyroid.
TSH is the major regulator of the thyroid
gland, it is a glycoprotein hormone which binds with receptors at the surface of
the thyroid follicular cell, this stimulates the release of T3 and T4
from the thyroid.
 TSH is the major regulator of the thyroid
gland, it is a glycoprotein hormone which binds with receptors at the surface of
the thyroid follicular cell, this stimulates the release of T3 and T4
from the thyroid.
TSH is the major regulator of the thyroid
gland, it is a glycoprotein hormone which binds with receptors at the surface of
the thyroid follicular cell, this stimulates the release of T3 and T4
from the thyroid.
The effects of low and high T3 blood levels on the rate of synthesis of the thyroid hormones can be seen in the diagram below.
For low T3 effects place mouse on picture.
Once released the thyroid hormones must be transported to the target cells throughout the body. T3 and T4 both have poor solubility in water so most of these hormones are bound to a carrier protein such as thyroxine-binding globulin when being transported in the blood. For the hormones to enter the cells, however, they must be free so they are released ready for target cell uptake. Bound forms of T3 and T4 remain in the blood.