

 |
 |
 Pantothenate Crystals Copied without permission from Roche Product Information |
Pantothenic AcidPantothenic acid, one of the water soluble B-vitamins, is essential in the body as a constituent of coenzyme A. Together with mercaptoethylamine, pantothenic acid makes up pantetheine. Pantetheine and adenosine-3',5'-diphosphate combine to give coenzyme A, which is important for synthesis of:
Did You Know? coenzyme A (coenzyme of acetylation) is required for many acyl group transfer reaction pathways. Top Chemical Structures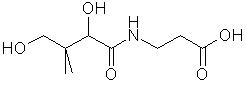 Fig.1 The Chemical Structure of Pantothenic Acid 3D Structure of Pantothenic Acid 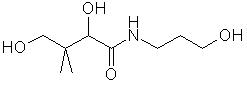 Fig.2 The Chemical Structure of Pantothenol Did You Know? Pantothenol is added to hair products as a moisturiser and conditioner. Top Principal Sources in FoodPantothenic acid is present in highest concentrations in:
Pantothenic Acid in the BodyAs part of coenzyme A, panthothenic acid is essential for:
StabilityPantothenic acid is easily destroyed by heat in acidic or alkaline conditions, but is stable in a neutral solution.Top SynthesisCondensation of D-pantolactone with P-alanine produces pantothenic acid and the addition of a calcium salt forms colourless calcium pantothenate crystals.Top (1) Source: Roche Product Information |