

 |
 |
 Vitamin D Crystals Copied without permission from Roche Product Information |
Vitamin DVitamin D, or calciferol, is the general name for a collection of steroid-like substances including vitamin D2, ergocalciferol (fig.1) and vitamin D3, cholecalciferol (fig.2). Found only in animal sources, vitamin D is fat soluble and can be manufactured by the body on exposure to UV radiation.Top Chemical Structures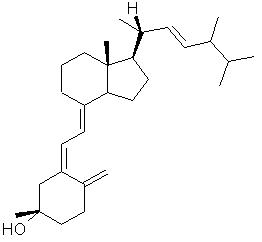 Fig.1 The Chemical Structure of Vitamin D2 (Ergocalciferol) 3D Structure of Vitamin D2 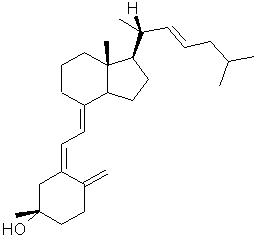 Fig.2 The Chemical Structure of Vitamin D3 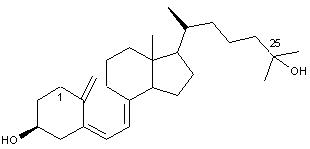 Fig.3 The Chemical Structure of Calcidiol 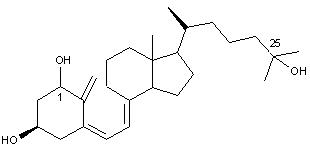 Fig.4 The Chemical Structure of Calcitriol Top Principal Sources in FoodVitamin D is only found naturally in animals and animal products; fruit and nuts contain no vitamin D at all. Richest sources include:
Did You Know? In many countries, products such as milk, margarine and vegetable oil are fortified with vitamin D, and provide a significant dietary source of the vitamin. Top Vitamin D in the BodyIn the body, the vitamin D is converted to its active hormone form by the liver and the kidney. The calciferol is converted to 25-hydroxycholecalciferol, calcidiol (fig.3), and then metabolized by the kidney to several active forms including 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol, calcitriol (fig.4).The main function of vitamin D in the body is to maintain blood levels of calcium and phosophorus. Vitamin D is essential for the absorption of these substances from the small intestine, and also for the mineralization process of the bones. The result of vitamin D deficiency is rachitis (rickets) in children and osteomalacia in adults. Top StabilityAs one of the fat soluble vitamins, vitamin D is stable in food storage, cooking and processing.Top SynthesisCholecalciferol is manufactured by irradiating 7-dehydrocholesterol with ultraviolet light. The production of ergocalciferol is similar, using a starting product of ergosterol, a yeast extract.Top |