

 |
 |
 Vitamin E Crystals Copied without permission from Roche Product Information |
Vitamin EThe name Vitamin E covers a collection of eight fat soluble compounds, tocopherols (methyl derivatives of tocol) and tocotrienols:
Did You Know? The word tocopherol comes from the Greek words tocos (childbirth) and pherein (to bring forth), after the essential role vitamin E plays in animal reproduction. The ending -ol is the standard chemical name ending for an alcohol. Did You Know?The antioxidant property of vitamin E is exploited when it is used as a stabliser in oil and fat containing foods. Did You Know? Vitamin E is used in cosmetics and skin products to prevent cell damage by UV light. Did You Know? Tocopherol is used in many pharmaceutical products as a stabiliser Did You Know? Some plastics, technical oils and greases contain alpha-Tocopherol as an antioxidant. Top Chemical Structures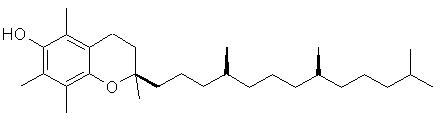 Fig.1 The Chemical Structure of alpha-Tocopherol 3D Structure of alpha-Tocopherol 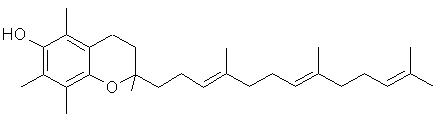 Fig.2 The Chemical Structure of alpha-Tocotrienol Top Principal Sources in FoodThe most important sources of vitamin E are:
Vitamin E in the BodyStored mainly in the fatty (adipose) tissues, the liver and in muscles, the principal role of vitamin E is as a powerful antioxidant, protecting body cells from the detrimental effects of free radicals and protecting unsaturated lipids against oxidation. Together with vitamin A and vitamin C, it forms the trio of antioxidant vitamins which are thought to help prevent cancer and cardiovascular disease. Vitamin E is also important in:
Top StabilityVitamin E is sensitive to heat, light and oxygen and significant losses have been found after relatively short times of food storage.Top Synthesis"Vitamin E derived from natural sources is obtained by molecular distillation and, in most cases, subsequent methylation and esterification of edible vegetable oil products. Synthetic vitamin E is produced from fossil plant material by condensation of trimethylhydroquinone with isophytol." (1)Top (1) Source: Roche Product information |