
Uses of solar cells
Space
Solar cells are very useful in powering space vehicles such as satellites and telescopes (e.g. Hubble). They provide a very economical and reliable way of powering objects which would otherwise need expensive and cumbersome fuel sources.

Image taken from www.space.com without permission
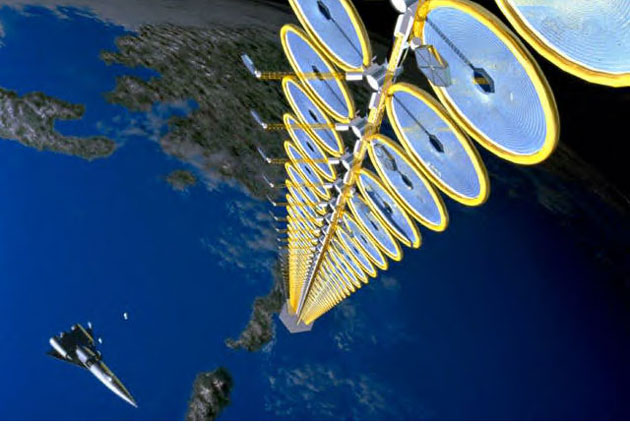
The above design for a solar cell array in space features many inflatable, fresnel reflectors which focus the Sun's light on small arrays of high efficiency cells.
The international space station is also another good example of solar cells being used in space. When it is finished, the station will have the most powerful solar array in space. Four sets of gold coloured wings (each one being 72 metres long and larger than the space station itself) will contain 250,000 solar cells and the whole array will be able to power a small neighbourhood. Some of the energy will be used immediately, such as in life support machines while some will be stored in batteries for when the station is not in use.

Image taken from www.cnn.com without permission
Solar cells are also being used to power the rovers which will be examining the surface of Mars in early 2004.
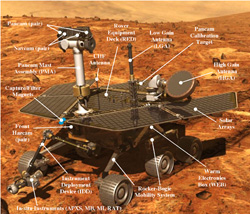
Image taken from: http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/ without permission
Solar powered vehicles
Solar powered cars are cars which are powered by an array of photovoltaic cells. The electricity created by the solar cells either directly powers the vehicle through a motor, or goes into a storage battery. Even if a vehicle is completely covered in solar cells, it will only receive a smaller amount of solar energy and will be able to convert only a small amount of that to useful energy. Because of this, most solar powered vehicles are only used in research, educational tools or to compete in the various races for solar powered vehicles.
The first solar powered car was built be Ed Passerini in 1977. Many large motor manufacturers have also put some serious research into solar cars. General Motors, for example, spent $8 million developing the "Sunraycer" (below). This car has a 90 square foot solar array incorporated into it's teardrop shaped body. Despite being 6m long, the total weight of the car is only 177kg due to light weight composites used in it's manufacture.

Image taken from www.gm.com without permission
Many races for solar powered vehicles occur throughout the year and serve to develop new technologies and show the public the idea of solar power as a viable power source. One of the first and most famous races is the World Solar Challenge; a 1872 mile race held in Australia. In 1996 Honda won with an average speed of 55.77mph. However, these kinds of average speeds can only be obtained with good weather conditions and huge investment in the vehicle. Production solar vehicles are still in their infancy and lots more research and development needs to be done before they can get close to the production line.