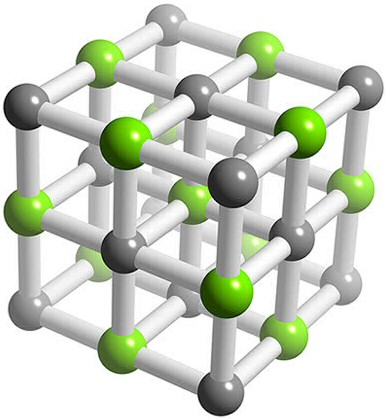
A mixture of Pancuronium Bromide, Sodium Pentothal and Potassium Chloride
|
Spokesman: After completion of last words, the injection is
administered. |
|
|
|
|
|
U.K. CERTIFICATE: 15 |
|
|
RUNTIME: 130 mins |
|
|
SYNOPSIS: David Gale (Kevin Spacey) is charged with rape and murder. Now Gale awaits execution, with a fatal injection of pancuronium bromide and potassium chloride. |
|
Speed of onset: Intermediate paralysis (2-3 mins) Mechanism of action: Pancuronium is a non-depolarising blocking agent that acts as competitive antagonist at the acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular junctions. It is a medium-term muscle relaxant and works by curarimimetic action. The quantity of acetylcholine released by the nerve impulse generally exceeds by that what is needed to elicit an action potential in a specific muscle fibre. Thus it is necessary to block 70-80% of the receptor sites before transmission fails. Medical use: With the appropriate intravenous dosage of this drug the effects last for approx. 40 minutes, which is used in combination with general anaesthesia during surgery for muscle relaxation. It is also used to optimize conditions for endotracheal intubation and assist ventilation.Main side effects:
This muscular relaxation may be hazardous if given to a patient that is seriously ill and it may accumulate, which in turn can lead to extended frailty. |
Click on the picture above
to interact
|
Potassium Chloride
|
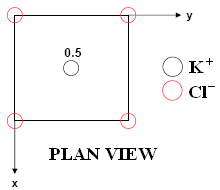
Crystal Structure: AX (NaCl - rock salt). Cubic close packing of anions (Cl-) with all octahedral holes filled by cations (K+). Importance: Potassium (K+) and chloride (Cl-) ions are key ions used within the human body, thus oral potassium chloride is taken to replenish supplies. Potassium ions are involved in muscle contractions as well as regulating fluid and electrolyte balance in cells within the body. It also keys a key role in the nervous system as it assists in sending nerve impulses. Furthermore it releases stored energy from protein, fat and carbohydrates during the process of metabolism. Chloride ions play a significant role in the central nervous system and are important in various biochemical systems, for instance GABA relies upon the entry of Cl− into particular neurons.Medical use: Potassium chloride is used to treat hypokalemia, digitalis poisoning, and as an electrolyte replenisher. Main side effects: Gastrointestinal problems |
Click on the picture above
to interact
|
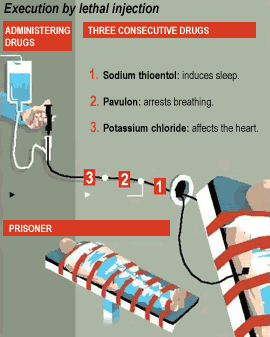
Execution by Lethal Injection
| Pancuronium is used as one component of a lethal
injection in capital punishment, within certain regions of the United States.
When it is administered with sodium pentothal anaesthetic, it causes this
anaesthetic to precipitate, rendering it ineffective.
So as pancuronium effectively collapses the diaphragm and lungs (arrests breathing). A massive overdose of intravenous potassium chloride is also used to stop the heart. Concern: Pancuronium possesses no sedative or analgesic effects, however the drug prevents the body from displaying pain. |
|