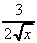 (g)
(g) 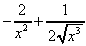
The aim of these is to give the students plenty of practice (and examples) of how the various differentiation rules work. Most should be fairly simple to work out (since all they're doing is applying the same rules again & again).
1. (a) -2/x2 (b) 1/x2 (c) -16/x5 (d) -24/x9 + 15/x4
(e) -6/x7 + 12/x13 (f) 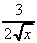 (g)
(g) 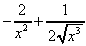
(h) 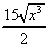 (i)
(i) 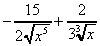 (j)
(j)
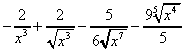
2. (a) dy/dx = 10x - 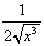 ,
when x=2 this has a value of 19.82
,
when x=2 this has a value of 19.82
(b) dp/dq = -3/q2 , when q=3 this has a value of -1/3
(c) dφ/dx = 1 - 1/(2x½) , when =1.2, this has a value of 0.544
(d) dZ/dζ = 6ζ + 1/(2ζ½) - (7/3)ζ4/3 , when =0.1, this has a value of 2.073
3. (a) 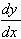 = -1 +2x which
equals 0 at x = ½, for which y = 2¾.
= -1 +2x which
equals 0 at x = ½, for which y = 2¾.
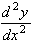 = 2, so that this point is a minimum.
= 2, so that this point is a minimum.
(b) 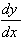 = 1 - 1/x2
which equals 0 at x = +1 with y = 2, or x = -1 with y = -2
= 1 - 1/x2
which equals 0 at x = +1 with y = 2, or x = -1 with y = -2
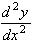 = 2/x3 with values of +2 and -2 respectively.
= 2/x3 with values of +2 and -2 respectively.
. Thus the first point is a minimum, and the second is a maximum.
(c) 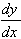 = -3x2
which equals 0 for x = 0 only, for which y = 8.
= -3x2
which equals 0 for x = 0 only, for which y = 8.
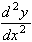 = -6x which is zero at this stationary point.
= -6x which is zero at this stationary point.
Thus examine the behaviour 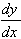 near the
stationary point. This is negative for x < 0, and
negative again for x > 0. Thus this is a horizontal
point of inflection.
near the
stationary point. This is negative for x < 0, and
negative again for x > 0. Thus this is a horizontal
point of inflection.
(d) 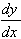 = 12x2
- 4x3 which has two roots at x
= 0 for which y = 0, and another at x = 3 for which y = 27.
= 12x2
- 4x3 which has two roots at x
= 0 for which y = 0, and another at x = 3 for which y = 27.
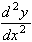 = 24x - 12x2
which is zero at x = 0 and negative at x = 3.
= 24x - 12x2
which is zero at x = 0 and negative at x = 3.
Examination of the gradient then establishes that the first point is a horizontal point of inflection, and the second is a maximum.
4. These first ones require the Product Rule.
(a) x(2x) + (x2+1).1 = 3x2+1
(b) 3x(-1/(2x)) + (5-x).3 = 15 - 3x
-  = 15 -
= 15 - 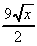
(c) (x2 + 1)(9x2 - 2) + (3x3 - 2x + 2).2x = (x2 + 1)(9x2 - 2) + (6x4 - 4x2 + 4x)
The next one requires use of the product rule twice!
(d) x(5x - 1)(14x) + (7x2 + 4) { x(5) + (5x - 1).1) }
= x(5x - 1)(14x) + (7x2 + 4)(10x - 1) = 14x2(5x - 1) + (7x2 + 4)(10x - 1)
(e) (x2 + 1/x)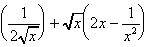
These next few require the Quotient Rule
(f) 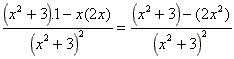 =
= 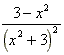
(g) 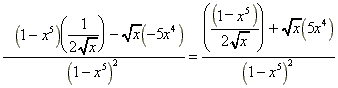
(h) 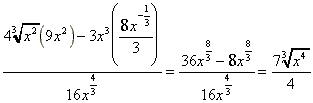
5. (a) Given that the concentrations vary with time as
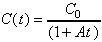 , then use the quotient rule to give:
, then use the quotient rule to give:
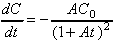
(b) If C0 = 0.06 mol.dm-3, and after 10 minutes C has fallen to 0.05 mol.dm-3, then from eqn (1):
(1 + 10A) = 0.06/0.05 = 1.2, A = 0.02 min-1.
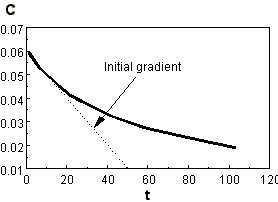
Substitution of this value and that of C0 with t = 0 into the derivative equation gives an initial rate of consumption of 0.0012 mol.dm-3.min-1.
Using the values of A and C0 in eqn (1), then after 25 minutes C0 will have fallen to