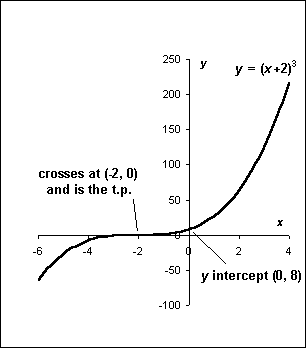1S Summer exam 2002 - Calculus Dr Paul May
1. Answer all parts (a) to (d).
Determine the following:
(a)
dy/dx if y
= 8x4 (1 mark)
(b) dy/dp if y = 6p5 + 3p – 2 (1 mark)
(c) db/dq if b = -7cos q (2 marks)
(d) dj/dk if j = 253e–27k (2 marks)
2.
Answer all parts (a) to (d). All parts carry equal marks.
Differentiate the following functions with respect to x, and simplify the result where possible:
(a) y = (7x + 2)(3 – 8x) (b) y = -5x7 ln x
(c) ![]() (d)
y = sin (5x6 – 2x2)
(d)
y = sin (5x6 – 2x2)
(8 marks)
3. Answer all parts (a) to (c).
Consider the function y(x) = (x + 2)3.
(a) Differentiate this function (without multiplying out the
brackets) and thence determine the co-ordinates (x,y) of the stationary
point(s).
(4 marks)
(b) Do the
stationary point(s) correspond to local maxima, minima, or point(s) of
inflection?
(4 Marks)
(c) Hence
sketch this function between x = -4
and x = +1.
(3 marks)
Answers
1) [1 mark for (a) and (b), 2 marks for the rest].
a) dy/dx = 32x3 b) dy/dp = 30p4 + 3
c) db/dq = +7sin q d) dj/dk = -6831 e-27k
2) [2 marks each].
a) Product Rule: (7x + 2).(-8) + (3 - 8x).7 = 5 –112x
b) Product Rule: -5x7(1/x) + (ln x).(-35x6) = -5x6(1 + 7ln x)
c) Quotient
Rule: ![]() =
= ![]()
d) Funct. of a Funct.: cos (5x6 – 2x2).(30x5 – 4x) = (30x5 – 4x) cos (5x6 – 2x2)
3)
a) Using Func. Of Func. Rule, dy/dx = 3(x + 2)2.(1) = 3(x + 2)2 [2 marks]
At the t.p. dy/dx = 0, so 3(x + 2)2 = 0, so there’s only 1 soln at x = -2.
Feeding x = -2 back into the original eqn, we get that the t.p is at: (-2, 0). [2 marks]
b) d2y/dx2 = 6(x + 2), and at x = -2 this has a value of 0. So the t.p. is a point of inflexion!
Checking the gradient either side of the t.p.: at x = -3, dy/dx = +3, so it’s increasing.
At x = -1, dy/dx = +3, so it’s increasing too. [3 marks]
c) When x is very large and +ve, y is v. large and +ve. When x
is large and –ve, y is large and –ve.
When x = -2, y = 0, and this is the t.p.
When x = 0, the intercept y = 8.
(The curve must be the right shape, the axes must be labelled, and the t.p. and y intercept must also be labelled to get the full 3 marks.)