1S Summer exam 2008 - Calculus Dr Paul May
1. Answer all parts (a) to (d). All parts carry equal marks.
Determine the following:
(a)
dy/dx if y
= 16x36
(b) du/dg if u = 1.7g3 + (3×106)g
(c) dΩ/dy if Ω
= 3tan y
(d) dñ/d– if ñ =
2 exp(–3–)
‑ 5–
(4 marks)
2.
Answer all parts (a) to (d). All parts carry equal marks.
Differentiate the following functions with respect to x, and simplify the result where appropriate:
(a) ![]() (b)
y = 12e-2x sin x
(b)
y = 12e-2x sin x
(c) ![]() (d)
y =
5 ln
(d)
y =
5 ln![]()
(8 marks)
3. Answer all parts (a) to (c).
Consider the quartic function: y = (x – 1)(x + 1)( x – 3)( x + 3)
(a) Multiply out the brackets in this equation.
(2 marks)
(b) Differentiate either version of this equation and hence find the co-ordinates of the stationary points.
(4 marks)
(c) Find the second differential of this equation, and hence find whether each of the stationary points is a local maximum, minima or point of inflection.
(3 marks)
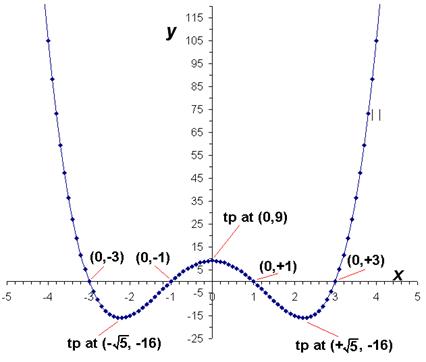
(d) Sketch this function between
x = ‑4 and x = +4.
(3 marks)
Answers
1)
a) dy/dx = 576x35 b) du/dg = 5.1g2 + 3×106
c) dΩ/dy = 3 / cos2y d) dñ/d– = ‑6 exp(‑3–) ‑ 5
2)
a) Rules for
Indices: y = ½x‑3 – x2/3 + 4x‑1/2
dy/dx = ‑(3/2)x-4 – (2/3)x-1/3
– 2x-3/2
= ![]()
b) Product Rule:
12e-2x ( cos x) + (sin
x) (-24e-2x) =
12e-2x (cos x ‑
2sin x)
c) Quotient
Rule: ![]()
d) Funct. of a
Funct.: dy/dx
= ![]()
Alternatively, by the Laws of Logs,
5 ln![]() is the same as ‑5 ln(2x2), so dy/dx =
is the same as ‑5 ln(2x2), so dy/dx = ![]()
3) (a) y = (x – 1)(x + 1)( x – 3)( x + 3) = x4 – 10x2 + 9
(b) dy/dx = 4x3 ‑ 20x
At the tps, dy/dx = 0, so 4x3 ‑ 20x = 0
x3 ‑ 5x = 0
x (x2 – 5) = 0
Therefore, x = 0 or (x2 – 5)=0, i.e. x = ±Ö5
When x=0, y = +9,
When x=+Ö5, y = ‑ 16,
When x= ‑ Ö5, y = ‑ 16.
So there are three turning points, at: (0, 9), (Ö5, ‑16), ( ‑Ö5, ‑16)
(c) d2y/dx2 = 12x2 ‑ 20
When x=0, d2y/dx2 = ‑20 (i.e. negative), so that the tp at (0, 9) is a maximum.
When x=+Ö5, d2y/dx2 = +40 (i.e. positive), so that the tp at (Ö5, ‑16) is a minimum.
When x= ‑Ö5, d2y/dx2 = +40 (i.e. positive), so that the tp at (‑Ö5, ‑16) is a minimum.
(d) Need to sketch graph, get correct shape, label axes properly, and label the turning points and places where it crosses the axes to get full marks.