1S Summer exam 2010 - Calculus Dr Paul May
1. Answer all parts (a) to (d). All parts carry equal marks.
Determine the following:
(a)
dy/dx if y
= 3x101
(b) du/dh if
u = 3.7h4 + (3×106)h2
(c) dΩ/dy if
Ω = 5 cos y
(d) dB/d$ if $
= 2 exp(7B)
‑ 5B2
(4 marks)
2.
Answer all parts (a) to (d). All parts carry equal marks.
Differentiate the following functions with respect to x, and simplify the result where appropriate:
(a) ![]() (b) y = 7e-2x sin x
(b) y = 7e-2x sin x
(c) ![]() (d) y =
ln
(d) y =
ln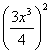
(8 marks)
3. Answer all parts (a) to (c).
Consider the function: y = 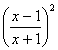
(a) Differentiate this equation and hence find the co-ordinates of the stationary point(s).
(4 marks)
(b) Find the second differential of this equation, and hence find whether the stationary point(s) is/are a local maximum, minima or points of inflection.
(4 marks)
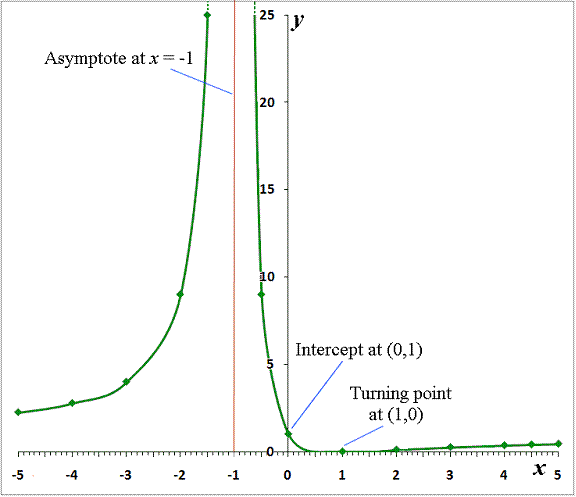
(c) Sketch the function between x = 5 and x = +5.
(4 marks)
Answers
1)
a) dy/dx = 303x100 b) du/dh = 14.8h3 + (6×106)h
c) dΩ/dy = 5 sin y d)
dB/d$ = ‑14 exp(‑7B) ‑ 10B
2)
a) Rules for
Indices: y = 6x-5/3 dy/dx = + (30/3)x-8/3
=
![]()
b) Product Rule: 7e-2x ( cos x) + (sin
x) ( 14e-2x) =
7e2x (cos x 2sin x)
c) Quotient
Rule: ![]() =
=![]()
d) Funct. of a
Funct.: dy/dx
= ![]() × 2
× 2![]() ×
× ![]() = 6 / x
= 6 / x
alternatively, rewrite it as y =
2 ln![]()
So that dy/dx = 2 × ![]()
3) (a) y = 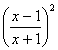
Use F-of-F Rule and then the Quotient Rule:
![]() = 2
= 2![]()
![]() =
= ![]()
At t.p. ![]() =0, so either 4(x
1) = 0 so
that x = +1, and y = 0,
=0, so either 4(x
1) = 0 so
that x = +1, and y = 0,
or ![]() , so that x = ¥ and y
= 1. This is an unusual solution and indicates
something odd happens at this point.
, so that x = ¥ and y
= 1. This is an unusual solution and indicates
something odd happens at this point.
So there are only 2
t.p.s, at (1, 0) and (¥, ‑1)
(b) d2y/dx2 = ![]()
(i) When x = 1, d2y/dx2 = 1/2, i.e. +ve so this is a minimum.
(ii) When x = ¥, d2y/dx2 is undefined
.
(c) Need to sketch graph, get correct shape, label axes properly, and label the turning points and places where it crosses the axes to get full marks.
From original eqn:
When x = 0, y = +1.
When x = 1, y = 0 (the p.o.i)
When x = 1 y = ¥ ; so have an asymptote at x = 1
When x = large and +ve, y = tends to +1
When x = large and -ve, y = tends to +1