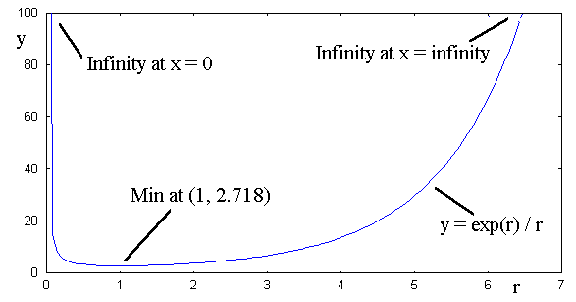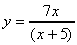 d) y = sin (2x2
- 9) (7 marks)
d) y = sin (2x2
- 9) (7 marks)
a) dy/dx if y = x3
b) dy/dm if y = 5m7 + m - 1
c) dy/dx if y = 8cos x d) dp/dq
if p = 1267e-q (7 marks)
2) Differentiate the following functions with respect to x,
and simplify the result where possible:
a) y = (x + 2)(x - 2) b) y = x2
ln x
c) 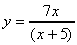 d) y = sin (2x2
- 9) (7 marks)
d) y = sin (2x2
- 9) (7 marks)
3) The function :
y = 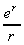 has stationary points at r = ± infinity
has stationary points at r = ± infinity
a) Differentiate this function and thence determine the co-ordinates
(y,r) of the remaining stationary point.
(6 marks)
b) The second differential of this function is: 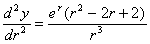
Determine whether the stationary point you just found is a local
maximum or minimum. (2 Marks)
c) Hence sketch this function between r = 0 and r =
infinity. (3 marks)
1) [1mark for (a), 2 marks for the rest].
a) dy/dx = 3x2 b) dy/dr = 35m6 + 1
c) dy/dx = -8sin x d) dp/dq = -1267e-q
2) [1 mark for (a), 2 marks for the rest].
a) Product Rule: (x + 2).1 + (x - 2).1 = 2x
b) Product Rule: x2(1/x) + (ln x).2x
= x(1 + 2ln x)
c) Quotient Rule: 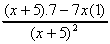 =
= 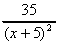
d) Function of a Function: cos (2x2 - 9).4x
= 4x cos (2x2 - 9)
3)
a) [6 marks in total]
Quotient Rule: rer - er / r2 = er(r - 1) / r2
For turning point, er(r - 1) / r2 = 0, so either: r2 = infinity r = ± infinity,
er = 0 r = - infinity
or (r - 1) = 0, r = 1
The last answer is the required one.
So the turning point is at (1, 2.718).
b) Determine the sign of the second differential, d2y/dr2. Putting in the value of r = 1, we get d2y/dr2 = e, which is +ve, so the t.p. is a local minimum. [2 marks]
c) Sketch: 3 marks (must get correct shape, and indicate t.p., and infinities).