 |
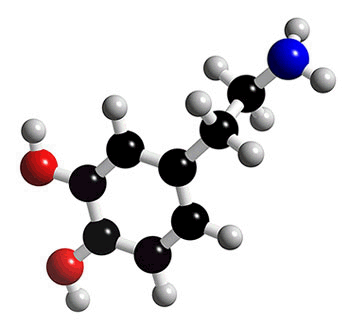
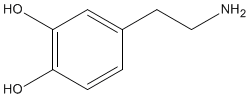
DOPAMINE |
 |
 |
DOPAMINE |
 |
Sian Gregory and Paul M. Burnham
Hillsborough College, Sheffield, UK
Molecule of the Month - October 2008
Also available: Chime Enhanced, VRML and JMol versions.
|
 |
 |
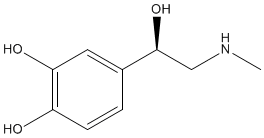 |
Dopamine |
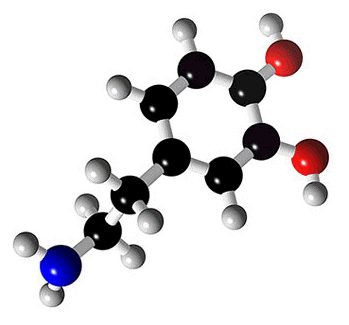
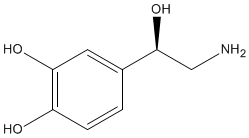
Norepinephrine |
Epinephrine |
| BIOSYNTHESIS |
The biosynthesis of dopamine is a two step process starting with the amino acid L-tyrosine. A second phenol group is added to the benzene ring of L-tyrosine forming levodopa, which is more commonly called L-dopa. This process is catalysed by the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase. Dopamine is formed by the removal of the carboxylic acid group from L-dopa. This is also an enzyme catalysed process and the enzyme involved is referred to, perhaps unsurprisingly, as dopa decarboxylase. |
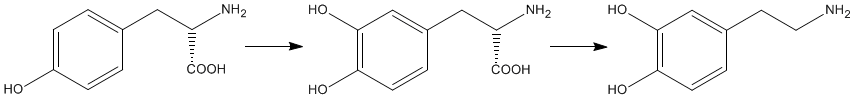 |
L-Tyrosine |
L-Dopa |
Dopamine |
There are many dopamine receptors in the brain and it is thought that dopamine is responsible for a general feeling of well-being. For example, dopamine has been linked with feelings of happiness, excitement and positivity as well as the eagerness to go after goals or rewards. Nicotine present in cigarette smoke increases the secretion of dopamine in the brain and hence relieves feelings of anxiety. Other drugs also increase dopamine levels in the brain, such as the amphetamine D-methamphetamine. Dopamine also has an important role in making smooth and controlled muscular movements. Changes in the levels of dopamine in the brain are linked with Parkinsonís disease. |
| DOPAMINE AND PARKINSON'S DISEASE | |
Parkinsonís disease is a degenerative neurological condition that progressively worsens. It is named after James Parkinson, a London doctor who was the first person to profile the disease in his ďEssay on the Shaking PalsyĒ. The condition generally affects movements like walking, writing, talking and swallowing. Symptoms may include repetitive shaking, slowness of movement and muscle stiffness. Parkinsonís is caused by the loss of nerve cells responsible for synthesising dopamine. Less dopamine is produced and consequently certain parts of the brain cannot function correctly. Symptoms will normally appear when 80% of the dopamine synthesising cells are lost. |
 |
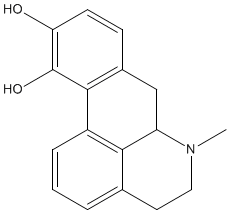 |
Apomorphine |
| BIBLIOGRAPHY |
|
![]() Back to Molecule of the Month page. [DOI:10.6084/m9.figshare.5426644]
Back to Molecule of the Month page. [DOI:10.6084/m9.figshare.5426644]