RESIDUES
Note: There are three (3) figures in this link. Please
use the scroll bar to see all three figures.
Introduction
This link displays the three residues that line the two (2)
types of channels in ferritin. As you look at the 3 residues, try
to determine the differences in them. These differences are what
leads to the 4-fold channel being hydrophobic and the 3-fold
channel being hydrophilic.
Leucine
Leucine is the amino-acid residue that lines the 4-fold
channel. This residue contains 2 functional groups that are
polar; COO-
and CNH3+.
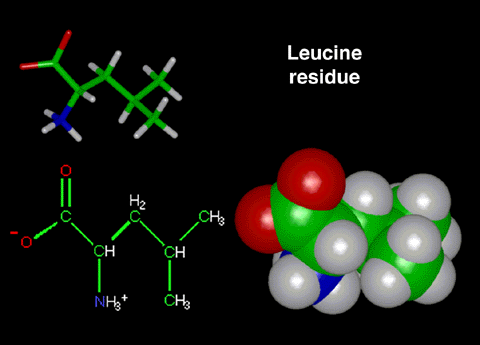 |
Figure 1:
This figure displays a stick representation, a
ChemDraw representation, and a CPK representation of the
amino-acid residue leucine (Zwitterionic form).
Note: The carbon atoms are green, the hydrogen
atoms are white, the nitrogen atoms are blue, and the
oxygen atoms are red in both models.
|
Glutamate
Glutamate is one of the amino-acid residues that line the
3-fold channel. This residue contains 3 functional groups that
are polar: 2 COO-
and 1 CNH3+.
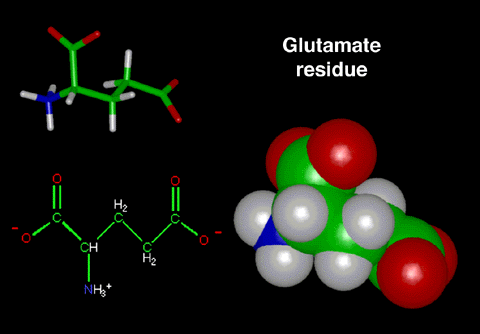 |
Figure 2:
This figure displays a stick representation, a
ChemDraw representation, and a CPK representation of the
amino-acid residue glutamate.
Note: The carbon atoms are green, the hydrogen
atoms are white, the nitrogen atoms are blue, and the
oxygen atoms are red in both models.
|
Aspartate
Aspartate is one of the amino-acid residues that line the
3-fold channel. This residue contains 3 functional groups that
are polar: 2 COO-
and 1 CNH3+.
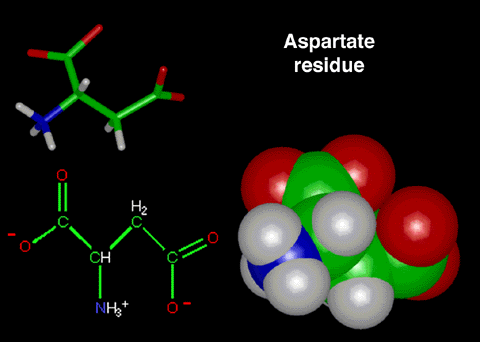 |
Figure 3:
This figure displays a stick representation, A
ChemDraw representation, and a CPK representation of the
amino-acid residue aspartate.
Note: The carbon atoms are green, the hydrogen
atoms are white, the nitrogen atoms are blue, and the
oxygen atoms are red in both models.
|
Return to Peptide-subunit Link
Return to Channel Link


