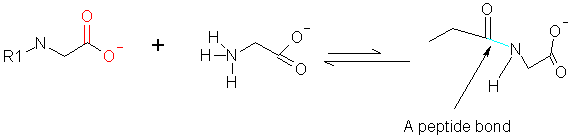
A peptide or amide bond is formed by joining an alpha - carboxyl group of amino acid 'A' to an alpha - amino group of amino acid 'B', this results in loss of a water molecule.

A polypeptide chain is formed by joining several amino acids, and each amino acid in this chain is called a residue. By standard convention, the amino end of the acid lies at the start of the chain, and hence the sequence of amino acids in the chain is written with the first amino-terminal residue.
For example AGW short for the tripeptide Ala-Gly-Trp, alanine is the terminal amino residue, and tryptophan is the carboxyl terminal residue. One thing to remember is that the side chains have unique R groups.