

 |
 |
 Vitamin A Crystals Copied without permission from Roche Product Information |
RetinolVitamin A is the collective name for a group of fat-soluble vitamins. The most useable form of the vitamin is retinol, often called preformed vitamin A as it is the active form in the body. Retinol (an alcohol) can only be found in animal sources and can be converted by the body into retinal (an aldehyde) and retinoic acid (a carboxylic acid), other active forms of vitamin A.Top Beta CaroteneBeta carotene, a hydrocarbon, is one of a family of dark pigments called provitamin A carotenoids, some of which can be converted to retinol by the body. In the liver, one molecule of beta carotene can be cleaved by an intestinal enzyme into molecules of retinol, so good food sources of beta carotene can also be good sources of retinol. The conversion of carotenoids to retinol will decrease when body stores are full thus preventing a retinol overdose, which can lead to toxic symptoms.Did You Know? About 700 naturally occurring carotenoids have been discovered! Did You Know? Carotenoids in plants act as light-absorbing pigments during photosynthesis and also help to protect cells against photosensitization. Top Chemical Structures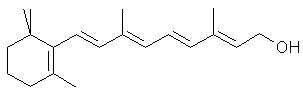 Fig.1 The Chemical Structure of Retinol 3D Structure of Retinol 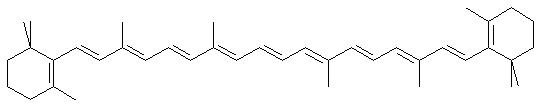 Fig.2 The Chemical Structure of Beta Carotene 3D Structure of Beta Carotene Top Principal Sources in FoodPreformed vitamin A, or retinol, is found in:
Top Vitamin A in the BodyVitamin A is essential in the body for maintaining the immune system and vision and also for growth and tissue differentiation. It is also thought to aid prevention of cancer.VisionThe retina of the eye is made up of light receptor cells, called rods, which allow us to 'see' light and dark. Within these cells is a pigment called rhodopsin which is a complex of opsin, a protein, and retinol. On exposure to light this complex disintigrates and releases electrical charges to the brain via the optic nerve. New rhodopsin is then formed from opsin and retinol.Immune SystemVitamin A aids health by maintaining the surface linings of the eyes and the intestinal, respiratory and urinary tracts, thus preventing bacteria from entering. It has also been suggested that vitamin A helps lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) to function effectively, and that carotenoids may act as antioxidants in the body.Tissue DifferentiationIn the body there are many different cells with many different functions. The process by which a cell becomes a specific type of cell is called differentiation, and vitamin A is essential for differentiation of epithelial cells (i.e those of the skin, the mucous membranes, the cornea and the blood vessel walls).Deficiency of vitamin A can result in:
Did You Know? Vitamin A deficiency is the leading cause of childhood blindness. Did You Know? The Ancient Egyptians knew that night blindness could be cured by eating liver - a food source later found to be rich in vitamin A. Top StabilityRetinol is sensitive to oxidation by the air. It is present in animal fats and oxidation of these can result in a loss of the fat soluble vitamin. Beta carotene is one of the more stable vitamins in foods. The compound is sensitive to heat but significant losses only occur after long periods of boiling.Top SynthesisVitamin A can be produced by extraction from fish-liver oil although the more common process is synthesis from beta-ionone.Top |