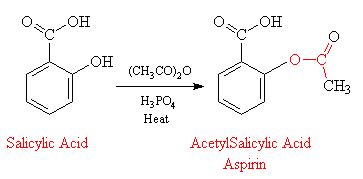
The acetyl group is shown in red.
One of the best known aromatic acetates is acetylsalicylic acid, or aspirin, which is prepared by the esterification of the phenolic hydroxyl group of salicylic acid.

The acetyl group is shown in red.
Aspirin possesses a number of properties that make it the most often recommended drug. It is an analgesic, effective in pain relief. It is also an anti-inflammatory agent, providing some relief from the swelling associated with arthritis and minor injuries. Aspirin is also an antipyretic compound, which means it reduces fever. Each year, more than 40 million lb of aspirin is produced in the US alone, a rate that translates to about 300 tablets per year for every man, woman and child. However, it is not so innocuous a drug as one might imagine from its widespread use and ready availability. Repeated use may cause gastrointestinal bleeding, and large doses can provoke a host of reactions including vomiting, diarrhea, vertigo and hallucinations. The average dose is 0.3-1 g; single doses of 10-30 g can be fatal.
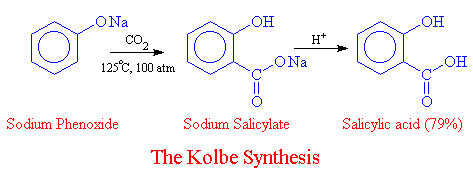
The key compound in the synthesis of aspirin, salicylic acid, is prepared from phenol by a process discovered over 100 years ago by the German chemist Hermann Kolbe. In the Kolbe synthesis (also known as the Kolbe-Schmitt reaction) sodium phenoxide is heated with CO2 under pressure and the reaction mixture is subsequently acidified to yield salicylic acid.
The mechanism by which aspirin relieves pain remained unclear for many years after its discovery. It is now believed to work by inhibiting the action of an enzyme called prostoglandin cyclooxygenase. This enzyme is involved with the synthesis of prostoglandins, which are hormones that amongst other things, modify the signals that are transmitted across the connections (synapses) between nerves. If these signals, particularly those conveying the sensation of pain, are blocked, so that they do not reach the brain, the person can no longer experience the pain. Prostoglandins may also help to dilate the blood vessels that cause the pain in headaches and migraines, so aspirin, by reducing the amount of prostoglandins in the system may also act as a preventative as well as a cure.