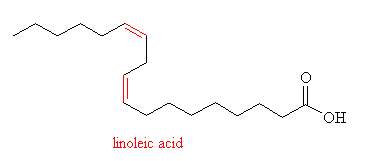
Linoleic Acid (also called cis,cis,-9,12-octadecadienoic acid) is an example of a poly-unsaturated fatty acid, due to the presence of two C=C double bonds. It is the main fatty acid found in vegetable oils such as soybean oil, corn oil and rapeseed oil. It is used for manufacturing margerine, shortening, and salad and cooking oils.

In order to convert the liquid linoleic oil (and its triglyceride) into soft solid margerine, hydrogen is bubbled through the oil in the presence of a nickel catalyst under fairly mild conditions (175-190°C, 20-40 p.s.i.). Hydrogenation in this way does a number of things. Firstly, hydrogen attaches to some of the double-bonded carbons, increasing the saturation level. In doing so, the molecules lose some of the rigidity associated with double bonds and so are able to flex. This allows them to pack closer together, raising the melting point, and turning the oil into a solid fat. The removal of some of the reactive double bonds in this way also reduces the chances of attack by oxygen, so that the fat becomes rancid much less readily, increasing its shelf-life. Superheated steam is then passed through the molten fat to remove any impurities (especially bad-smelling acids and aldehydes). But since this process also removes the coloration from the fat, artificial colouring agents made from carotenes of various kinds are added to make it appear yellow and buttery. Other additives include butanedione (to make it smell like butter), vitamins A and D, emulsifiers (to sharpen the flavour) and binding agents (lecithins) to hold the whole thing together.
Hydrogenation like this also has an unwanted effect - it can lead to isomerisation of the double bond, from cis to trans. An example of this is shown in the diagram, in the two forms of 9-octadecenoic acid (another component of vegetable oil), the cis form (oleic acid) and the trans form (elaidic acid), the double bond is shown in red.
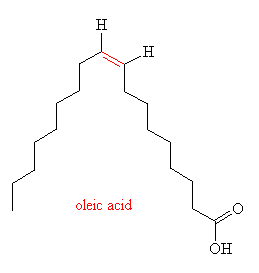
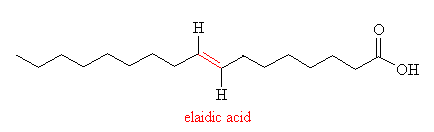
Since the trans acids are straighter than their bent cis isomers, they can pack together easier and so have a higher melting point. By selecting a particular hydrogenation catalyst, temperature, stirring speed and pressure, manufacturers can control the precise composition of the margerine to create a particular 'mouth feel', melting range and stability. The primary source of trans-fatty-acids (TFAs) in the western diet is hardened vegetable oils, which typically contain 35-50% of TFAs, compared to less than 5% in butter. However, unlike the cis acids, which occur naturally, the trans acids are artificial and so cannot be metabolised in the human body as efficiently as their isomers. Over the past 3 decades TFAs have been linked to cancer, diabetes, heart disease, low birth rate and obesity. However, these results are still controversial, as a number of other studies (funded by the US soybean industry) have concluded that TFAs are as safe as their cis counterparts. So, in the question of which is the healthiest to spead on our toast - butter, containing saturated fats which have been linked to coronary disease and strokes, or margerine, with the possible risks associated from TFAs, - well, the jury is still out...