Synthesis
Hydrazine can be made on an industrial scale by the Raschig synthesis. This is the reaction between ammonia and sodium hypochlorite. The reaction occurs in two steps, the first step being the formation of chloramine and sodium hydroxide from the two reactants, and the second step involving a reaction between ammonia and the chloramine synthesised in the first step.
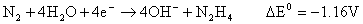
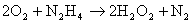
There is however a competing reaction between the hydrazine formed and the chloramine produced in the first step. This can be suppressed by adding gelatine to the reaction mixture.
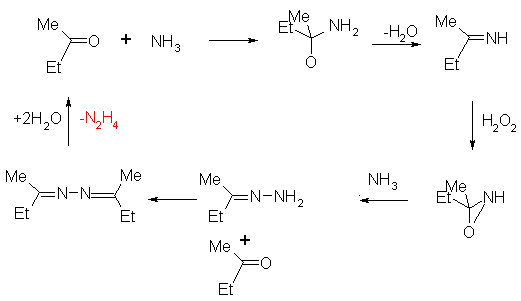
An improved synthesis involves the reaction of ammonia with a urea and is shown below