The Joy of Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the study of the movement and the separation of charges in matter. Without electrochemistry modern life today would be very different.
 Contents
Contents
Luigi Galvani; the first electrochemist
![]()
Imagine life today
without the battery, no cars, no mobile phones, no torches, no walkmans, in
fact no portable electrical appliances at all!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! In fact batteries
have been produced commercially for over a century and there is a wide range of
power and size, from 0.1Wh miniature cells to 10MWh load levelling batteries.

A battery is a
cell, which converts chemical energy into electricity. The electron transfer
that occurs in a redox reaction is transferred into an electric current.
A common battery is the Alkaline battery i.e. Duracell battery. This battery consists of a Zinc electrode and a Manganese oxide electrode and an alkaline electrolyte.
The redox reaction that the battery relies on is the oxidation of the Zinc and the reduction of the manganese:
Zn ® Zn2+ + 2e-
MnO2 + 2H2O + 2e- ® 2MnOOH +2OH-
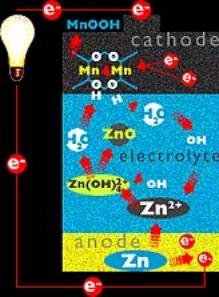
The alkaline cell was first developed during the 1950’s but is closely based on the Leclanche cell that was developed during 1870-1890. The major difference between the alkaline and Leclanche cell is that the alkaline cell has an improved electrolyte, aqueous KOH.
The Leclanche cell had the over discharge of:
Zn + 2MnO2 + 2H2O + ZnCl2 ® 2MnOOH + 2ZnOHCl
There are 2 main
types of battery
- Primary cell: use once
and then discard.
- Leclanche cells
- Alkaline cells
- Lithium batteries
- Secondary cell:
rechargeable as redox reaction is reversible.
- Pb/Acid
- NiCd
- Lithium ion
A common use of secondary cells is the car battery, which is used for starting the internal combustion engine. The car battery is rechargeable and has lead and lead oxide electrodes and a strong acid electrolyte.
![]()

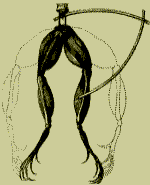
Luigi Galvani was a medical student who became Professor of
Anatomy at the University of Bologna and it was quite by accident that he
discovered Bioelectricity. In 1780 Galvani conducted experiments using frogs legs
and found that when an electric charge was applied to the nerves or muscles the
muscles contracted. The electric charge came from an electrostatic machine
called a Leyden jar. Galvani was also able to cause contraction of the muscles
in the absence of a charge, which led him to conclude that this was a new form
of electricity produced by living tissue.
Insert a hyperlink
Insert a hyperlink
![]()


Alessandro Volta (1745-1827) was a friend of Galvani’s although his
ideas differed slightly. Volta believed that the results from Galvani’s
experiment were due to the salt liquids of the frog’s insides completing a
circuit with the metal electrodes and producing electricity. The electricity
came form the two metal electrodes toughing in a moist atmosphere as opposed to
Galvani who thought that the legs themselves were creating electricity.
Following Galvani’s experiment Volta built the worlds first battery in
1800, the Voltaic pile. It consisted of alternating layers of Zinc, Silver and
a separator of blotting paper soaked in salt water.
Type some text.
Office phone
Type some text.
![]()
Add a description.
Add a project.
Add a description.
![]()
Type some text.
![]()
Type some text.
![]()
Last Revised:
