![]()
When tissue is damaged two coagulation pathways, the intrinsic and the
extrinsic, start to enable blood to clot.
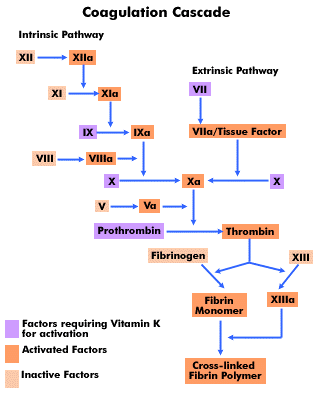
![]()
The intrinsic pathway occurs in the plasma, it is activated by exposure
of blood to negatively charged surfaces such as collagen. A conformational
change in factor XII (Hageman factor) results in the conversion of prekallikrein
to kallikrein. Kallikrein activates factor XII to XIIa by reciprocal proteolytic
activation. Factor XIIa catalyses the conversion of factor XI (plasma
thromboplastin antecedent) to XIa. High-molecular-weight kininogen acts
as a cofactor for all these reactions by binding factor XI and prekallikrein
to the activating surface.
Factor XIa then activates factor IX (Christmas factor) to IXa, IXa then activates factor X (Stuart-Prower factor) with the platelet membrane phospholipid providing the template and factor VIII (anti-haemophilic factor) acts as a cofactor. Xa then activates factor II (prothrombin) to IIa (thrombin) using the cofactor V (labile factor). These two steps both require calcium ions. Thrombin then cleaves factor I (fibrinogen) into fibrin monomers that form unstable polymers. Factor XIII (fibrin-stabilising factor) is activated by thrombin and calcium ions, this catalyses the formation of covalent bonds between fibrin molecules therefore making a stable form of fibrin.
There are other ways the intrinsic pathway can be activated. Factor XI can also be activated by thrombin and factor VIIa of the extrinsic pathway may convert factor IX to its active form IXa.
![]()
When tissue is damaged factor III (tissue factor;TF) is released, this
complexes with factor VII (proconvertin) in the presence of calcium ions.
The TF-VIIa complex then activates factor X to Xa.
The pro-cofactors V and VIII are activated by thrombin by positive feedback and at the same time protein C may be activated to limit coagulation via negative feedback.