Previous
page
How
does thyroxine enter cells?
The uptake of T3 and T4
into the cells is by 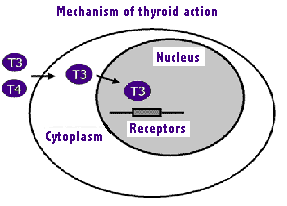 a specific
carrier-mediated uptake across the plasma
membrane. The process is both energy and sodium dependent, as the plasma
membrane transporter is a Na+ dependent organic anion
transporter. Diffusion is a process ruled out for crossing the plasma membrane
in this case as the mean radii of T3 and T4 are both
greater than the pore radius of plasma membrane.
a specific
carrier-mediated uptake across the plasma
membrane. The process is both energy and sodium dependent, as the plasma
membrane transporter is a Na+ dependent organic anion
transporter. Diffusion is a process ruled out for crossing the plasma membrane
in this case as the mean radii of T3 and T4 are both
greater than the pore radius of plasma membrane.
The rate of uptake into cells determines the
rate at which T3 is produced from T4 this in turn causes
effects such as a change in oxygen consumption and a change in the rate of
burning of proteins, carbohydrates and lipids.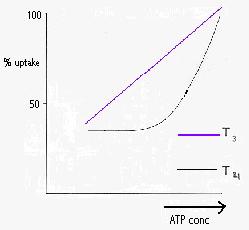
If the amount of ATP in the body
tissue decreases (i.e. a decrease in the bodies calorie uptake) there is a
decrease in in cellular uptake of T3 and T4. Two days of
fasting can inhibit T3 uptake into some cells by 40%. Uptake can also
be inhibited by some substances such as fatty acids.
Next
page
 a specific
carrier-mediated uptake across the plasma
membrane. The process is both energy and sodium dependent, as the plasma
membrane transporter is a Na+ dependent organic anion
transporter. Diffusion is a process ruled out for crossing the plasma membrane
in this case as the mean radii of T3 and T4 are both
greater than the pore radius of plasma membrane.
a specific
carrier-mediated uptake across the plasma
membrane. The process is both energy and sodium dependent, as the plasma
membrane transporter is a Na+ dependent organic anion
transporter. Diffusion is a process ruled out for crossing the plasma membrane
in this case as the mean radii of T3 and T4 are both
greater than the pore radius of plasma membrane.