
NUCLEAR REACTIONS AND RADIOACTIVE DECAY.
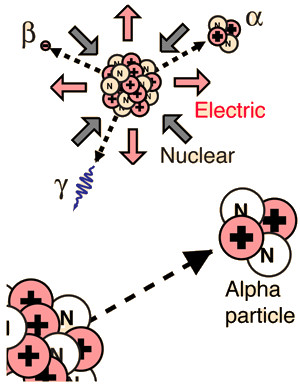 A nuclear reaction differs to that of a chemical reaction. In chemical
reactions, the nuclei of the atoms from the reactants to the products
is unchanged. In nuclear reactions, the protons and neutrons are
rearranged in the nucleus of the atom to form new elements. Radioactive
substances give off three types of radiation; alpha particles, beta
particles and gamma rays.
A nuclear reaction differs to that of a chemical reaction. In chemical
reactions, the nuclei of the atoms from the reactants to the products
is unchanged. In nuclear reactions, the protons and neutrons are
rearranged in the nucleus of the atom to form new elements. Radioactive
substances give off three types of radiation; alpha particles, beta
particles and gamma rays.
ALPHA DECAY:-
When the nucleus of an atom has too many protons it results in
disequilibrium of the nucleus due to the excessive repulsion. In order
to reduce the repulsion the atom emits an alpha particle. An alpha
particle consists of 2 protons and 2 neutrons and is identical to a
Helium nucleus. If an atom emits an alpha particle the atomic number is
reduced by two and the molar mass by four.
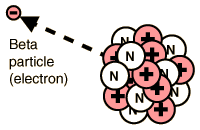
BETA DECAY:-
When the neutron to proton ratio in the nucleus is too great a beta
particle is emitted. In basic beta decay a neutron is transformed into
a proton and an electron. The electron is then emitted as a beta
particle which increases the atomic number by one and the molar mass is
unchanged.
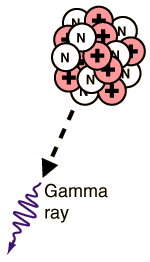
GAMMA DECAY:-
When the nucleus of an atom is at too high an energy it reaches
equilibrium by emitting an electromagnetic photon of energy known as a
gamma ray. The loss of a gamma ray does not alter the atomic number or
the molar mass of the element, the atom simply passes to a lower state
of energy.
|Example of decay series. |Contents page. |
Picture Sources -
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/nuclear/imgnuc/alprad2.gif
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/nuclear/imgnuc/betarad.gif
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/nuclear/imgnuc/gamrad.gif