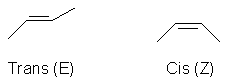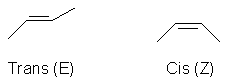Isomer Classification
Isomer:
molecules that have the same molecular formula but different molecular structure.
- There are two types of isomer, structural and stereo.
- Stereo isomerism can be either optical, geometric, or conformational.
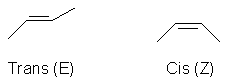
- Optical isomerism occurs when the molecule has a chiral centre (four different groups attached to a central carbon).
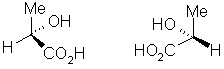
Chirality results in non-superimposable mirror images, also known as enantiomers.
- Enantiomers are chemically identical except for the way they interact with other chiral molecules.