Cellular
Synthesis of Cholesterol
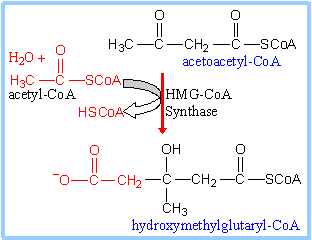
The precursor molecule for the synthesis of cholesterol is Hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme
A (HMG-CoA). It is formed formed by
condensation reaction between acetyl-CoA and acetoacetyl-CoA, catalyzed by HMG-CoA
Synthase. This is illustrated in reaction
scheme 1 below:
Scheme
1

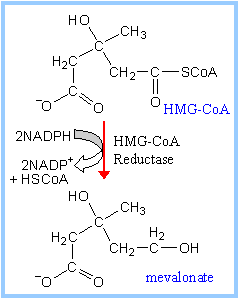
Mevalonate is then formed in a reaction
(scheme 2) catalysed by the enzyme
HMG-CoA Reductase,
which is an integral protein of endoplasmic reticulum membranes.
The carboxyl group of
hydroxymethylglutarate that is in ester linkage to the thiol of coenzyme A is
reduced to an aldehyde and then to
an alcohol.
NADPH
acts as a reductant in this 2-step reaction:
Scheme
2
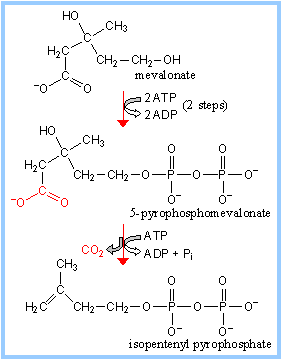
Mevalonate is phosphorylated by 2 sequential
phosphate transfers from ATP, before
ATP-dependent decarboxylation, with dehydration, yields isopentenyl
pyrophosphate
Scheme
3
Isopentenyl Pyrophosphate Isomerase
inter-converts isopentenyl pyrophosphate and dimethylallyl
pyrophosphate
via a mechanism involving deprotonation and protonation.
Prenyl Transferase
then
catalyzes a series of head-to-tail condensation reactions.
Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate reacts with isopentenyl
pyrophosphate to form geranyl
pyrophosphate.
Scheme
4 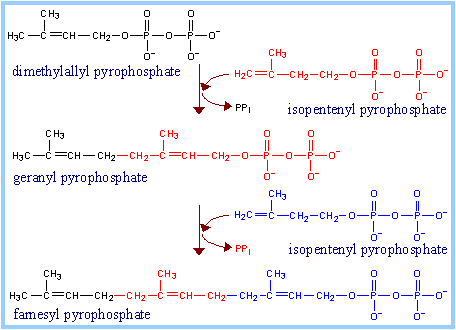
Squalene Synthase
catalyzes head-to-head condensation of 2 molecules of farnesyl pyrophosphate,
with reduction by NADPH, to yield squalene.
Scheme
5
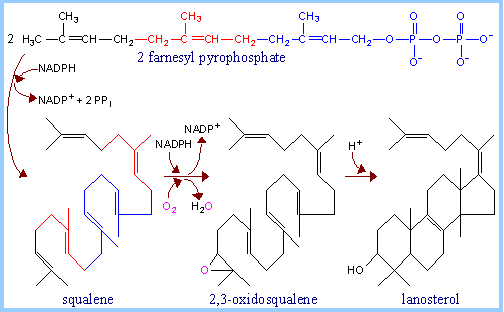
Squalene
is oxidised to 2,3-oxidosqualene,
with the reaction catalyzed by Squalene epoxidase.
NADPH acts as reductant and O2
as oxidant- one atom of oxygen is incorporated into the substrate (as the
epoxide) and the other is reduced to water.
A
series of electron shifts are catalyzed by Squalene Oxidocyclase.
The shifts are initiated by donation of a proton to the epoxide and lead to cyclization
giving the sterol product, lanosterol.
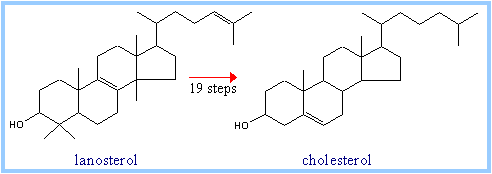
Conversion of lanosterol to cholesterol
occurs via 19 reactions. These are catalyzed by enzymes associated with endoplasmic
reticulum membranes, some of which are members of the cytochrome
P450 enzyme superfamily.
Scheme
6
Illustrations:http://www.rpi.edu/dept/bcbp/molbiochem/MBWeb/mb2/part1/cholesterol.htm