CARBON NANOTUBES
Mmmm..... sounds dull I hear you cry, but I beg you to read on through my small introduction to the world of nanotechnology.
Why, well this chemical technology has the potential to improve the world around you, if you can understand the potential
of this technology then this is the closest a scientist can come to seeing into the future.
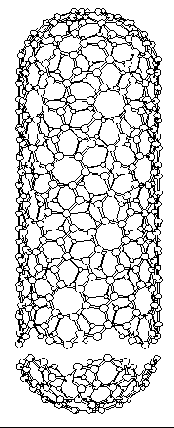
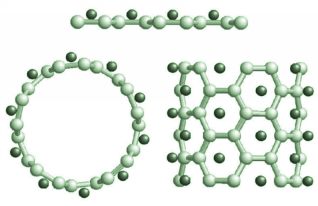
Carbon nanotubes are basically rolled up sheets of graphite that form tubes that are only nanometers in diameter, these tubes can be capped by placing half of a fullerene molecule on the end. There are two types of basic nanotube the single-wall nanotube(like right) and the multi-wall nanotube(like left) which is much the same but is made up of multiple layers of graphite.
To synthesise multi-wall nanotubes do arc evaporation(in an inert atmosphere of argon and helium) and electrolysis, the multi-wall nanotubes will be found at the cathode. To synthesise single-wall nanotubes you simply have use the same process but add a metal such as cobalt.
Below is link to an mpeg simulation showing some of the likely steps and reactionary intermediates involved in the formation of a double wall nanotube(note does not accurately represent the physical reality):
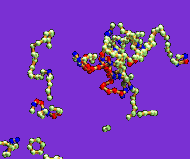 Double-wall carbon nanotube formation movie
Double-wall carbon nanotube formation movie
Image and mpeg taken from http://www.pa.msu.edu/~tomanek/nanotubes
There are also two different shapes of nanotube that can form the straight nanotube or the skewed nanotube like a drinking straw. These two shapes have very different conductivities the straight having metallic conductivity and the skewed has semi-conductivity.
So far I don't expect 100% of you to of found this interesting but this is where you start to find out what all this could actually mean to you. Because this material can have many different properties it has a wide range of future uses which I cannot cover here, but here are just a few reasons why you should be excited about this material:
- Nanotubes ropes and fibres: When this is perfected this will be the future of carbon fibres as these are approximately 100 times stronger than steel wool and one quarter of the density. Currently these nanoropes are made by laser-evaporation of graphite enriched by a nickel-cobalt alloy which forms many single-wall nanotubes which bundle together to form strong nanoropes. Imagine in the future if you could crash your car with virtually no consequences!(for the car).
- Nanowires:Technology in consumer products requires everything to be small when these conductive nanotubes can be grown into small nanowires this could greatly reduce the size of your mobile phone or computer.

- Nanotube flat screen display devices:For all you t.v. fans, a research team at Mie University in 1997 discovered that carbon nanotubes emit ring-shaped electron discharges when exposed to a weak electrical field. All very clever but in 1999 a process was developed for growing carbon nanotubes aligned vertically on base plates of field emission displays(FED). This technology could lead to the high quality flat screen televisions you might be watching in the future.
- Nanotubes as tubes:One of the most obvious use of these hollow chemically inert nanotubes is as nano-pipelines to transport individual molecules. This could be used to transfer specific molecules into individual cells much like a miniture hypodermic needles. The nanotubes only capped at one end can be used as nano-sized test tubes for studying reactions involving small numbers of molecules. The simulation below shows a C60 buckyball within a fully capped nanotube:
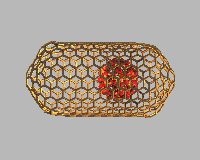 Switching a nanotube-based memory element
Switching a nanotube-based memory element
Image and mpeg taken from http://www.pa.msu.edu/~tomanek/nanotubes
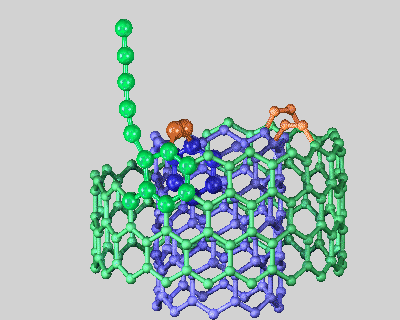
- Nanotube functionality:The surfaces of the nanotubes can be fuctionalised, this can be oxidising the terminal carbon on the surface of nanotubes to a carboxylic acid group then this can be further functionalised. The actual graphite surface itself will only react with very reactive species. To the right is a picture of the structure of a nanotube that was formed from Boron and Berylium. All this shows the amount of possible new research that can be done in functionalising nanotubes in new ways and also creating nanotubes from totally different materials, some of this research will undoubtably lead to more uses of nanotubes in future technology.
As this is such a large subject which still hasn't been explored fully I suspect that my site hasn't satisfied your need for information on this subject, so click on the links page to the left and you will find that I have links to some pages that may give you a place to start finding further information.
 Double-wall carbon nanotube formation movie
Double-wall carbon nanotube formation movie 

 Double-wall carbon nanotube formation movie
Double-wall carbon nanotube formation movie 
 Switching a nanotube-based memory element
Switching a nanotube-based memory element 