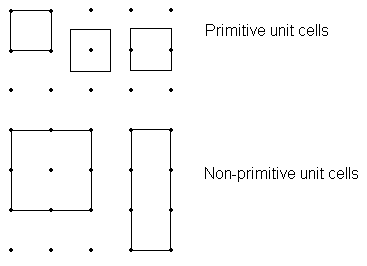
An ideal crystal is constructed by the infinite repetition of identical structural units. In the simplest crystals the structural unit is a single atom, for example in solid metals such as copper and iron. The structure of a crystal is defined in terms of a lattice with the structural unit or ‘basis’ attached to each ‘lattice point’. The lattice points form a set such that the structure is the same as seen from each point.
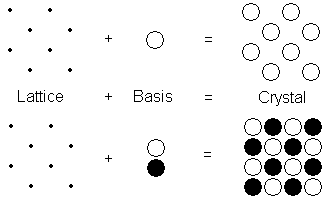
Figure 1: Illustration in 2 dimensions of the construction of a crystal from a lattice and a basis. The dots represent lattice points. Notice that the same lattice can be used to form different crystals by using different bases.