|
UBIQUITIN |

|
Biological Functions |
|
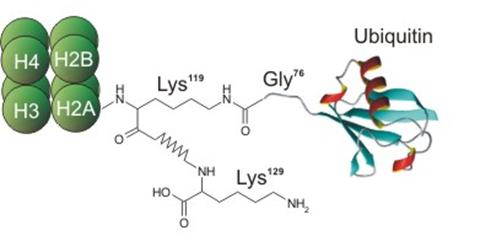
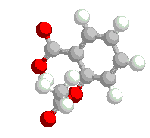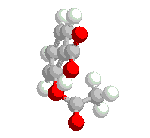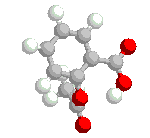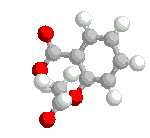
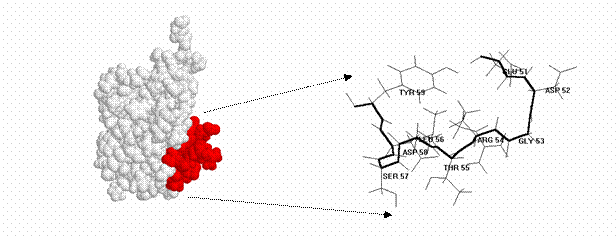
Ubiquitin and its ubiquitinylation pathway can be a part of different biological processes, like: • Cell cycle - some proteins which are degraded In ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis serve regulatory functions in the cell. (e.g. ubiquitin is attached to cyclin during the G1 phase of mitosis). By controlling the concentration of key proteins by selective degradation ubiquitin is a main tool of regulatory system of eukaryotic cells. • Lymphocyte differentiation promoting factor - ubiquitin stimulates differentiation of both B and T lymphocyte cell populations [3]; • Transfer protein - intracellularly, monoamine oxidase A and B are found tightly associated with the outer membrane of the mitochondria, where they are inserted by ubiquitin, with energy provided by adenosine triphosphate ATP [28]; • Heat shock protein - as a response of organisms against rapid temperature increase bigger expression of ubiquitin is observed. It is supposed that ubiquitin proteolyses badly folded/expressed proteins, which were created during shock, also protects cells against oxidative stress [24,27]; • Ubiquitin Cross-Reactive Protein - is necessary in primary response of cells to interferon [25]; • Component of PHF (Paired Helical Filament) - this component is present near nucleus in neurons of people suffering from Alzheimer’s or Down disease. Fact that ubiquitin is a component of PHF is supposed to be connected with ubiquitin and ATP dependent proteolysis which is responsible for degradation of NFT (Neuro-Fibrillary Tangles - big aggregates of PHF present near nucleus)fragment [26,31]; Figure 9. Mono-ubiquitinylated nucleosome. • Gene expression regulator - H2A histone is mono-ubiquitinylated in actively transcribed region, and not proteolysed, what suggests that ubiquitin can have the influence on genes expression [4,5]; • The maintenance of chromatine structure - H2A histone is mono-ubiquitinylated, and not proteolysed, what suggests that ubiquitin can have the influence on chromatin conformation [4,5]; • Immunophilin - it has been shown that ubiquitin acts as immunophilin binding tacrolimus (FK506) and sirolimus (rapamicin) with Kd’s of 0.8 and 0.08 nM, respectively. It is also known that the ubiquitin complexed with tacrolimus inhibits calcineurin phosphatase [43]. Figure 10. Three-dimansional structure of ubiquitin with exposed fragment of 51-59. • Immunomodulator - in recent years it was noticed that fragments of ubiquitin can also work outside of the cell. 51-59 ubiquitin fragment (Fig. 10) is able to decrease a humoral and cellular immune response. The shortest immunosuppressory active fragment was found to be 52-56. Asp52 amino acid of 52-56 peptide (Asp-Gly-Arg-Thr-Leu) can be replaced by Alanine without the loss of biological activity [29]. Therefore the residue 52 can be used in further modifications [44]. Some of analogues of 51-59 fragment of ubiquitin present activity comparable to cyclosporin A or FK506, which are used as common immunosuppressive drugs for people after organ transplants [29]. • Ribosome biogenesis - ubiquitin is often expressed in the cells as a single copy of ubiquitin fused to some ribosomal proteins, like L40 or S27A. After translation fused proteins are cleaved from ubiquitin. |