As a simple example, we will expand our molecular
orbital as a linear combination of just two atomic orbitals (this could, for
example, be the two 1s AOs in the
hydrogen molecule):
![]() (5)
(5)
Now substituting into eq. 2 we obtain:
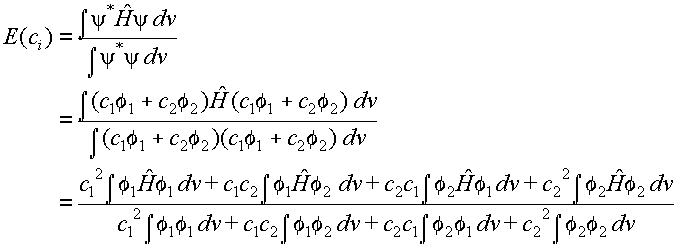 (6)
(6)
Eq. 6 now simplifies to give:
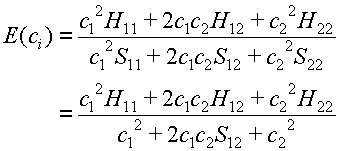 (9)
(9)
This can be rewritten in the form:
![]() (10)
(10)
Now differentiating eq.10 with respect to c1
we obtain:
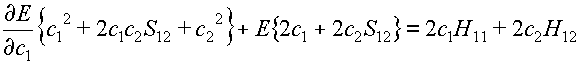 (11)
(11)
We now set 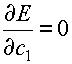 to obtain:
to obtain:
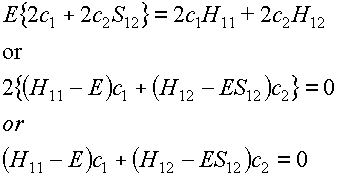 (12)
(12)
If we differentiate eq.10 with respect to c2
we obtain the equation :
![]() (13)
(13)