Other examples of
aromatic molecules:
Cyclopropenyl cation:
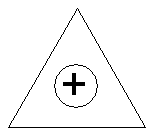 (i.e. C3H3+)
(i.e. C3H3+)
Only 2 p electrons;
both can go in the lowest energy MO (orbital with energy a + 2b).
Total p electron
energy
= 2´(a +2b)
= 2a +4b
Delocalization energy of cyclopropenyl radical
= (2a+4b) – (energy of
1 double bond, (2 p electrons))
= (2a+4b) –(2a + 2b)
= 2b (same as benzene)
· So C3H3+
is predicted to be stable.
· It is aromatic
with 4n+2 (n = 0) p
electrons.
Experimentally:
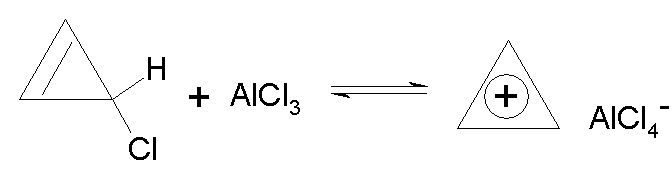
· Cyclopropenyl
cation is found to be relatively stable.
· It can be
synthesized as shown above, and isolated.
· The triphenyl
derivative has been crystallized and its structure determined by X-ray
crystallography. C-C distances all
equal, 1.40Å, similar to benzene (1.39Å).