How does the program know when to stop?
i.e. how does it know when it has
reached a minimum?
Convergence
criteria are used to test if the minimization has converged
For example:
· monitoring change
in energy from one step to the next, stop the minimization when the change
falls below a threshold
· monitor change in
coordinates, stop when structure is changing only a little
· stop when the
root mean square of the gradient is small,
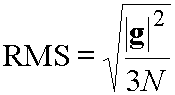 , i.e. the square
root of the gradient (with respect to the coordinates) squared divided by the
number of coordinates.
, i.e. the square
root of the gradient (with respect to the coordinates) squared divided by the
number of coordinates.
· The biggest
element of g is also monitored