· Remember that
normal mode analysis makes the approximation that the potential energy surface
is harmonic (i.e. quadratic).
· Good
approximation for deep, well-defined minima, but it is less good for ‘looser’ degrees
of freedom found in large ‘floppy’ molecules.
· Within this
approximation, the normal modes can be used to calculate thermodynamic
properties.
· Geometry
optimization gives a static structure - vibration of the molecule and the
effects of temperature should be included.
· We know that a
harmonic oscillator must have zero-point energy. The zero point energy of our molecule can be calculated as
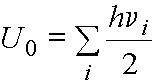 (11)
(11)
summing over the i normal modes. From the
calculation above, the zero-point energy of water is 64 kJ/mol.