
 |
 |
 Niacin Crystals Copied without permission from Roche Product Information |
NiacinNiacin (nicotinic acid and the amide derivative nicotinamide) is one of the water soluble B-vitamins. In the blood, brain, kidney and liver it is converted to the coenzymes nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP), both of which are involved in the generation of energy in cells. Tryptophan is an amino acid which is a provitamin of niacin.Top Chemical Structures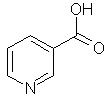 Fig.1 The Chemical Structure of Nicotinic Acid 3D Structure of Nicotinic Acid 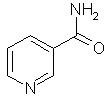 Fig.2 The Chemical Structure of Nicotinamide 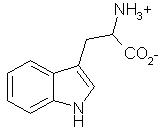 Fig.3 The Chemical Structure of Tryptophan Top Principal Sources in FoodBoth forms of niacin are widely occurring in nature. Nicotinic acid is the predominant form in plants and nicotinamide in animals. The major dietary sources of niacin are:
Niacin in the BodyDeficiency of niacin results in a disease called Pellagra, the symptoms of which include:
Did You Know? An earlier name for niacin was PP factor (pellagra-preventative factor). Top StabilityNicotinic acid and nicotinamide are both stable to light, heat, air and alkali.Top SynthesisNiacin can be synthesised by the oxidation of 5-ethyl-2-methylpyridine. A method for producing nicotinamide via 3-methylpyridine uses the starting products acrolein and ammonia.Top |