

 |
 |
 Vitamin B2 Crystals Copied without permission from Roche Product Information |
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2, or riboflavin is an intermediary the transfer of electrons in the cellular oxidation-reduction reactions which generate energy from protein, carbohydrate and fat. The riboflavin coenzymes are also important for the transformation of vitamin B6 and folic acid into their respective active forms, and for the conversion of tryptophan into niacin.Did You Know? Earlier names for this water soluble vitamin were lactoflavin, ovoflavin, hepatoflavin and verdoflavin, indicating the sources (milk, eggs, liver and plants) from which the vitamin was first isolated. Top Chemical Structure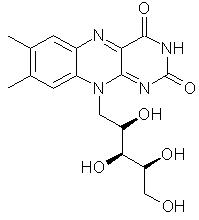 Fig.1 The Chemical Structure of Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) 3D Structure of Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) Top Principal Sources in FoodRiboflavin is very widely occurring in nature, present in all animal and plant cells. However, there are few sources which are rich in riboflavin. The highest concentrations are in yeast and liver but the most common dietary sources include:
Vitamin B2 in the BodyRiboflavin is the precursor of flavoproteins:
StabilityRiboflavin is sensitive to light but is heat stable.Did You Know? The use of ethylene oxide in food sterilisation can destroy riboflavin. Top h3>Synthesis There are two methods of manufacture of riboflavin:
Top |