

 |
 |
 Vitamin C Crystals Copied without permission from Roche Product Information |
Vitamin CVitamin C, or ascorbic acid is one of the water soluble vitamins.Did You Know? Most animals can synthesize their own ascorbic acid within their liver, with the exception of fish, primates (including humans) and Guinea pigs! Did You Know? Vitamin C is commonly added to foods as an antioxidant to protect colour and aroma. Did You Know? Vitamin C in an alkaline solution can be used as a photographic developing agent. Did You Know? As a reducing agent, ascorbic acid is used industrially in metallurgy. Top Chemical Structure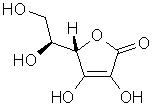 Fig.1 The Chemical Structure of Ascorbic Acid 3D Structure of Ascorbic acid Top Principal Sources in FoodGood sources of ascorbic acid in nature include:
Vitamin C in the BodyVitamin C is vital for the production of Collagen. (Click on the "Rasmol" icon in this link to view the 3D structure of collagen) Collagen is the intercellular substance that gives bones, teeth, cartilage, blood vessels and muscles their structure. Ascorbic acid is needed for synthesis of bile acids; it also maintains skin elasticity, aids in iron absorption, and improves resistance to infection. Symptoms of beginning vitamin C deficiency include:
Top StabilityIn food, ascorbic acid can be partially or completely destroyed by overcooking or long periods of storage as it is sensitive to heat, light and oxygen.Top SynthesisVitamin C can be extracted from plant sources, such as rose hips or blackcurrants, but is more commonly synthesized from glucose.Top |