What is Sonochemistry?
Chemistry is the interaction of energy and matter. Yet there are surprisingly few ways of putting energy into molecules to drive reactions. One of the newest, ultrasound, uses the principles of acoustic cavitation in the formation, growth, and violent collapse of bubbles in a liquid called ''single bubble sonoluminescence''
Life as a chemist might not be as exciting as Keanu Reeves, suggested in the 1996 movie Chain Reaction. In that 20th Century Fox thriller, a Nobel laureate and his grad student discover a way of using sonochemistry to catalytically produce unlimited quantities of hydrogen from plain water- and get caught in a chain reaction of murder and high-tech espionage.
Unlike researchers in the movie, this real-life breed of chemists is constrained by realities such as the laws of thermodynamics. Even so, they are driving some very exotic reactions under extreme conditions. There are plenty of exciting practical applications althought not quite on a scale of the new source of clean, limitless enery described in Chain Reaction
|
|
Sonochemistry, or the use of ultrasound in chemistry, has been with us for around 80 years but there was a great resurgence in interest in the early 1970s. At this time many chemists began to examine the effect of ultrasound on reactions and applications to organic chemistry in particular became commonplace. Many reactions which were normally sluggish, or indeed did not proceed at all, could be mediated by bathing the reaction in ultrasonic waves.
|
This means that chemical reactions that take place under more conventional conditions are accelerated, or even yield totally different products. The reason for this can be due to either physical or chemical effects of cavitation.
| The physical effects can enhance the reactivity of a
catalyst by enlarging the surface area, or accelerate a reaction by proper
mixing of reagents.
The amount of things that can be accomplished with sonochemistry is, at this stage, only limited by the minds of those working with sonochemistry. It is a whole new field of research that is growing very fast, with exciting prospects for any researcher. |
|
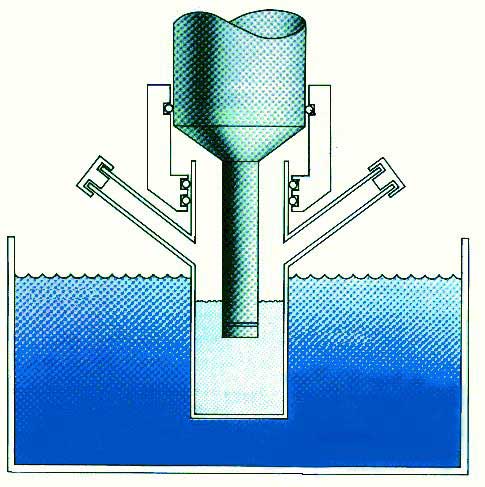
| Fig1 - typical sonochemical apparatus |
pictures from
http://www.scs.uiuc.edu/~suslick/britannica.html