Synthesis
The first total
syntheses of beta-carotene were reported in 1950 by
Karrer and Eugster, Inhoffen et al and Milas et al .
There are now many methods known, and beta-carotene is produced industrially
on a large scale.
Beta-carotene contains 40 carbon atoms, ie it is a C40 carotenoid. There are numerous methods of joining two or three smaller molecules to give the required carbon skeleton. These can be classified as symmetric or unsymmetric. An example of a symmetric synthesis would be
Beta-carotene contains 40 carbon atoms, ie it is a C40 carotenoid. There are numerous methods of joining two or three smaller molecules to give the required carbon skeleton. These can be classified as symmetric or unsymmetric. An example of a symmetric synthesis would be
C16
+ C8 + C16 = C 40
whereas an unsymmetric
synthesis would be
C25
+ C15 = C40
Here are two examples of industrial syntheses. The first was developed by the Badische Anilin- & Soda-Fabrik ( BASF) and is based on the Wittig reaction. The second is a Grignard reaction, elaborated by F. Hoffman-La Roche & Co. Ltd ( Roche) from the original synthesis of Inhoffen et al. They are both symmetrical; the BASF synthesis is C20 + C 20 , and the Roche synthesis is C19 + C2 + C 19 .
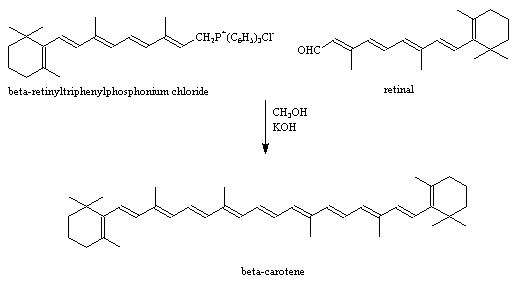
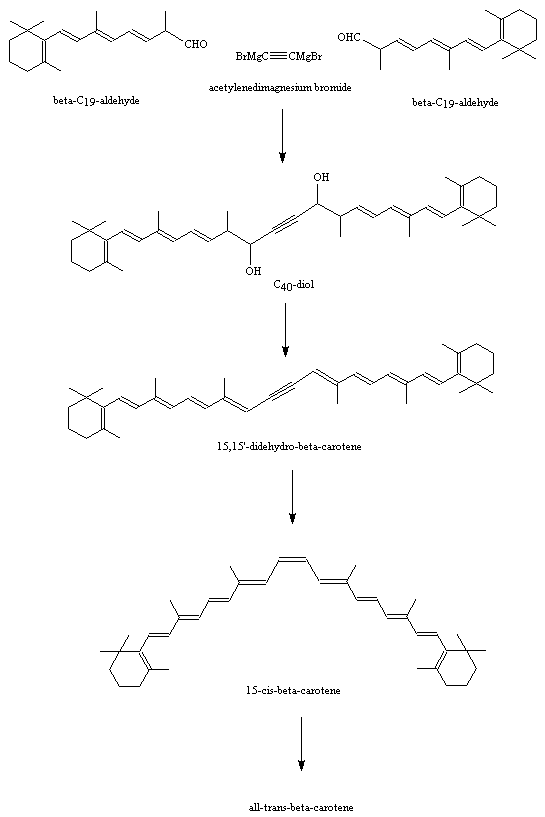
Here are two examples of industrial syntheses. The first was developed by the Badische Anilin- & Soda-Fabrik ( BASF) and is based on the Wittig reaction. The second is a Grignard reaction, elaborated by F. Hoffman-La Roche & Co. Ltd ( Roche) from the original synthesis of Inhoffen et al. They are both symmetrical; the BASF synthesis is C20 + C 20 , and the Roche synthesis is C19 + C2 + C 19 .
BASF Synthesis

Roche synthesis
