|
Key
Data and Description
History
Geological Information
Crystallography
Reactions of Platinum
Platinum Compounds
Uses
Platinum
Market
Links
and Resources |
Uses

Throughout the world, platinum jewellery
is made in a purity of at least 85% platinum, and in Europe and the
USA, 95% is the norm. Other platinum group metals - palladium,
ruthenium and iridium - and copper and cobalt are commonly alloyed
with platinum to optimise its working characteristics and wear
properties.
One of the main advantages of platinum for jewellery
fabrication is its strength and resistance to tarnish. It can be
repeatedly heated and cooled without hardening and oxidation
effects, while even the most slender sections of platinum
permanently retain their shape, providing a secure setting for
diamonds and giving jewellery designers a freedom of invention not
always possible with other materials.
Platinum has the ability, in certain
chemical forms, to inhibit the division of living cells. The
discovery of this property in 1962 led to the development of
platinum-based drugs to treat a wide range of cancers. Cis-platin,
[PtCl2(NH3)2], the first platinum
anti-cancer drug, was first used in 1977 for the treatment of
certain types of cancer such as leukaemia or testicular cancer.
Platinum can be fabricated into very
tiny, complex components. As it is inert, platinum does not corrode
inside the body, while allergic reactions to platinum are extremely
rare. Platinum also has good electrical conductivity, which makes it
an ideal electrode material. Platinum electrodes are used in
pacemakers which treat irregular heart disorders.
Catheters are flexible tubes which
can be introduced into arteries and they contain platinum marker
bands and guide wires, which are used to help the surgeon guide the
device to the treatment site. The radio-opacity of platinum, which
makes it visible in x-ray images, enables doctors to monitor the
position of the catheter during treatment.

Platinum medical wires
Autocatalysts are used to remove major exhaust
pollutants from the exhaust lines of many vehicles.
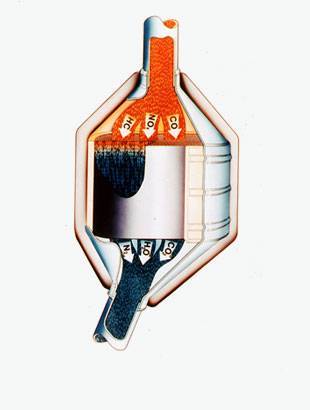
An autocatalyst
An autocatalyst consists of a
cylinder of circular or elliptical cross section made from ceramic
or metal formed into a fine honeycomb and coated with a solution of
chemicals and platinum group metals and mounted inside a stainless
steel canister.
The principal use of nitric acid is
the for the production of nitrogen fertilizers.
The first step in the production of
nitric acid is the oxidation of ammonia gas with air to form nitric
oxide using a platinum-rhodium catalyst.
Platinum catalysts are employed in
the manufacture of silicones. Addition of a platinum compound to the
silicone mixture catalyses the cross-linking process which results
in the formation of a silicone product with the desired properties.
Silicones are durable materials with
excellent chemical and fire resistance. They are also pliable,
waterproof and electrically insulating. Consequently, silicone
materials have a large number of uses in everyday life.
Platinum, and to a much greater
extent palladium, are mixed with gold or silver as well as copper
and zinc to produce alloys for dental inlays, crowns and bridges.
The hard discs in hard drives are
usually coated with a cobalt based alloy, but platinum is added
which enhances the magnetic qualities of the cobalt alloy, enabling
data to be stored at higher densities and improving access times
hence improving the data storage capacity of hard drives.
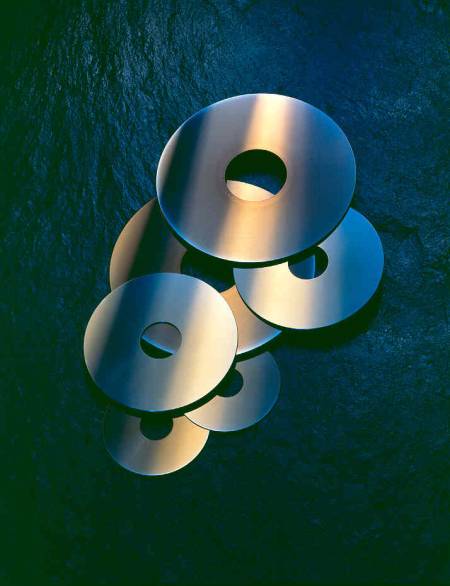

Platinum coated
computer hard drive disks
Platinum and platinum alloys are used
in the manufacture of vessels that hold, channel and form molten
glass, because platinum's high melting point, strength and
resistance to corrosion allow it to withstand the abrasive action of
molten glass. Additionally, they do not react with glass nor
do they oxidise at high temperatures.
Platinum is used in reinforced glass
fibres, liquid crystal displays (LCDs), cathode ray tube displays
(CRTs) used in TVs and visual display units in computers, optical
and ophthalmic glass, container glass where more platinum is used
for more corrosive glass, and ceramic glass used for example in
electric cooker hobs.
Other platinum uses are listed below:
-
Coating missile nose cones, jet
engine fuel nozzles.
-
Used as a catalyst in the contact
process for the production of sulphuric acid, for cracking oil and
as a catalyst in fuel cells.
-
Platinum wires glow red hot when
placed in the vapour of methanol, thereby acting as a catalyst to
convert the alcohol into formaldehyde. This is used to produce
cigarette lighters and hand warmers.
-
Carbon monoxide detectors.

Carbon monoxide
detectors
All images in this section
are courtesy of www.platinum.matthey.com
|