
Acetylcholine is transmitted at the nerve-muscle junction by cholinergic nerves. Cholinergic nerves are part of the parasympathetic nervous system.
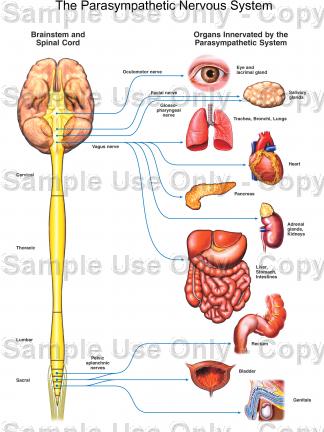
Taken from: www.catalog.nucleusinc.com
The parasympathetic system is part of the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS), which is comprised of two antagonistic nerves; the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems.
The parasympathetic system is concerned with the conservation and restoration of energy. It is responsible for causing reductions in heart rate and blood pressure, and it facilitates digestion and the absorption of nutrients, it is consequently responsible for the excretion of waste product.
An overview of the responsibilities of the two systems is shown below:
| Function | Sympathetic System | Parasympathetic System |
| Heartbeat | Increases | Decreases |
| Pupil Size | Dilates | Constricts |
| Salivation | Decreases | Increases |
| Bronchioles | Dilates | Constricts |
| Digestive Juices | Inhibits | Stimulates |
| Tear Ducts | No comparable effect | Increased secretion of tears |
| Bladder | Relaxes | Constricts |