 CVD Diamond-Fibre-Reinforced Composites
CVD Diamond-Fibre-Reinforced Composites
We are investigating methods to fabricate diamond-fibre-reinforced matrix composite materials for possible use in advanced aerospace applications. The diamond fibres are made as described previously, and photos can be seen on the SEM photos page.
Metal Matrix Composites (MMCs)
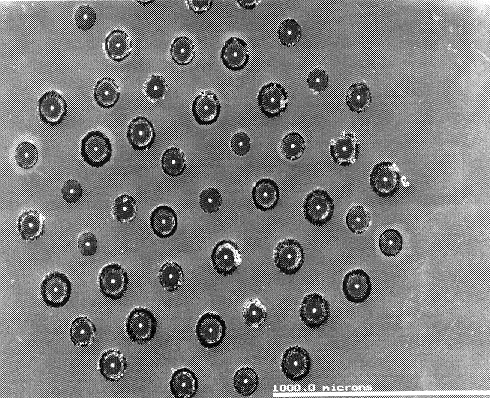
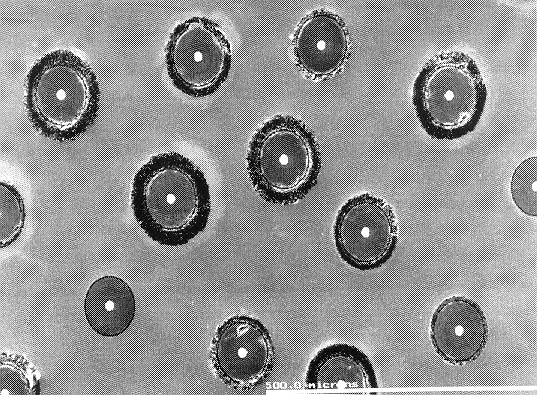
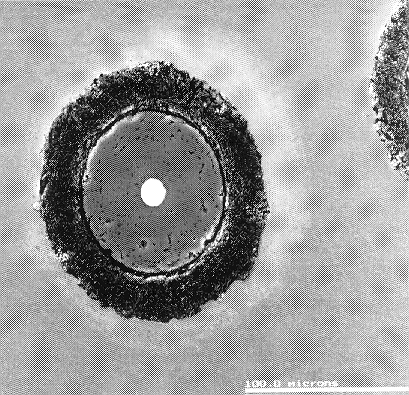
MMCs are composites where the matrix material is a metal, for example Ti, reinforced with diamond fibres. The MMCs are made by a process called Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) at Farnborough. The SEM photos below show various pictures at increasing magnification of a Ti-alloy MMC reinforced with a number of diamond-coated Textron (SiC) fibres.
 |
 |
 |
 |
In this case the diamond fibres were long (10 cm) and aligned in the same direction. This provides a huge increase in stiffness in one direction (i.e. anisotropically), and the composite has the advantage of being lightweight.
Plastic Composites
We have also made a number of plastic composites reinforced with diamond fibres. The plastic chosen was perspex (PMMA) since this was easily made in the lab, was transparent, and had a Young's modulus significantly smaller than that of the diamond fibres. We found that only 1% volume fraction of diamond fibres would increase the Young's modulus of the composite bar by a factor of six! In these composites, around 100 aligned diamond fibres were used.
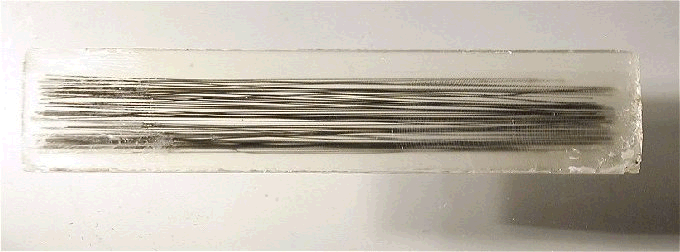 |
The world's first plastic (PMMA) composite reinforced with about 100 diamond fibres. Actual size is 100x20x5 mm. |
 |
Side view of another PMMA composite, with 2 layers of diamond fibre reinforcement. |
Plastic Thermal 'Heat Pipes'
Plastic composites with aligned diamond fibres do not conduct electricity, but do conduct heat well along the direction of the fibres. The heat travels rapidly down the length of the diamond coatings to a heat sink at the other end of the composite bar, raising the possibility of using these composites as 'heat pipes' - removing the localised heat from an electronic device and conducting it to an exterior radiator without any of the heat leaking out laterally and damaging nearby sensitive components.
Related Papers
- P.W. May, C.A. Rego, R.M. Thomas, M.N.R. Ashfold, K.N. Rosser, P.G. Partridge and N.M. Everitt, "Preparation of Solid and Hollow Diamond Fibres and the Potential for Diamond Fibre Metal Matrix Composites", J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 13 (1994) 247-9.
- P.G. Partridge, P.W. May, C.A. Rego and M.N.R. Ashfold, "Potential for Diamond Fibres and Diamond Fibre Composites", Mater. Sci. Technol., 10 (1994) 505-512.
- P.G. Partridge, G. Lu, P. May and J.W. Steeds, "Potential High-Strength High Thermal Conductivity Metal-Matrix Composites Based On Diamond Fibres", Diamond Relat. Mater. 4, (1995) 848-851.
- M.N.R. Ashfold, P.W. May, E.D. Nicholson, P.G. Partridge, G. Meaden, A. Wisbey and M.J. Wood, "The Potential for Diamond Fibre Composites", Applications of Diamond Films and Related Materials: 3rd Int. Conf. 1995, Editors: A. Feldman, Y. Tzeng, W.A. Yarbrough and M. Murakawa (NIST Special Publication 885, Washington 1995), pp529-531.
- N.M. Everitt, R. Silva, J. Vieira, C.A. Rego, C.R. Henderson and P.W. May, "Friction Measurements on Hot Filament CVD Diamond Films deposited on Etched Tungsten Carbide Surfaces", Diamond Relat. Mater. 4, (1995) 730-734.
- P.G. Partridge, M.N.R. Ashfold, P.W. May and E.D. Nicholson, "The Effective Chemical Vapour Deposition Rate of Diamond", J. Mater. Sci., 30 (1995) 3973-3982.
- G.H. Lu, P.G. Partridge and P.W. May, "A Technique for the Manufacture of Long Hollow Diamond Fibres by Chemical Vapour Deposition", J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 14 (1995) 1448-1450
- G. Meaden, P. G. Partridge, M.N.R Ashfold, E.D Nicholson, A Wisbey, "Laser Cutting of Diamond Fibres and Diamond Fibre / Titanium Metal Matrix Composites", Diamond Relat. Mater. 5 (1996) 825
- G. Meaden, P.G. Partridge, M.N.R. Ashfold, E.D. Nicholson and A. Wisbey, "Laser Ablation of diamond fibres and a Diamond Fibre Metal Matrix Composite", J. Mater. Sci., 31 (1996) 2801-2805.
- E.D. Nicholson, G. Meaden, E. Kalaugher, P.G. Partridge, M.N.R. Ashfold, P.W. May and A. Wisbey, "Continuous Diamond Fibres and Diamond Fibre-Reinforced Composites", Diamond Films and Technology, 6 (1996) 217.
- G. Meaden, P.G. Partridge, E.D. Nicholson, J. Nicholson, A. Wisbey and M.N.R. Ashfold, "Diamond-Fibre Metal Matrix Composites", Diamond Relat. Mater. 6 (1997) 898
- P.W. May, M. Hall and D. Smith, "Diamond Fibre Reinforced Plastic Composites", Int. J. Mod. Phys. B. Cond. Matter, 16, (2002) 906-11.
- P.J.C. Wigg, P.W. May and D. Smith, "Stiffness Measurements of Diamond Fibre Reinforced Plastic Composites", Diamond Relat. Mater. 12 (2003) 1766-70.
- P.W. May, R. Portman, K.N. Rosser, "Thermal Conductivity of CVD Diamond Fibres and Diamond Fibre Reinforced Epoxy Composites", Diamond Relat. Maters. 14 (2005) 598-603.
