 |
Top view of a polycrystalline CVD diamond film grown using the Hot Filament method on a Si substrate. Process gas mixture was 1% methane in H2. |

| Cross-section of a 100 µm-thick CVD diamond film grown by DC arc jet. The columnar nature of the growth is clearly evident, as is the increase in film quality and grain size with growth time. |
 |
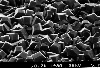
With higher methane concentrations, the crystal size decreases and form rounded
structures. This is a nanocrystalline diamond film grown using 3% methane in H2. |
 
|
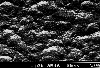
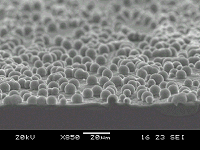
With even higher methane concentrations, the crystal size decreases further and becomes smooth. This is a nanocrystalline diamond film (top view and cross-section) grown using 5% methane in H2. |


 |
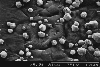
Sometimes nanocrystalline diamond grows in rounded 'ballas' (ball-like) structures, and this is called 'cauliflower' diamond. |
|
The initial stages of nucleation of diamond, this time on a Ni substrate. |

| Diamond grown at lower substrate temperature - now the crystals are predominantly (111) triangular facetted. |
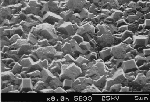
 
| Films grown with 1% methane in hydrogen, plus, top: 0.5% N2, middle: 1%NH3, and bottom: 3%NH3. The nitrogen content changes the film morphology to become predominantly (100) square facets, unless the N concentration becomes too high when the film becomes nanocrystalline (as in the bottom picture). |
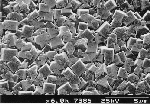
| A film grown with methane hydrogen plus 0.2% PH3. The film morphology has again become predominantly (100) square facets. |
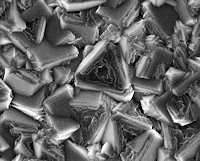
| A triangular crystallite showing internal step-edge growth 'rings'. |
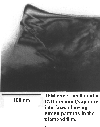
| A TEM cross-section of a diamond film grown on sapphire. The stresses in the diamond crystals, caused by thermal expansion mismatch on cooling, show up as interference patterns. |
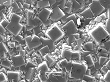
| An SEM showing combined microcrystalline diamond plus nanocrystalline diamond. |
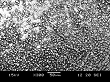
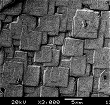
| SEMs showing diamond grown onto HPHT diamond. The growth has produced square (100) pillars. You can also see an animation of this (16 Mb!). |
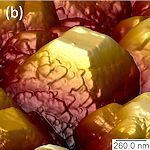 |
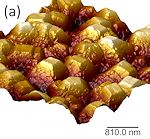
AFM images of a microcrystalline diamond film, giving a better idea of the topology. |

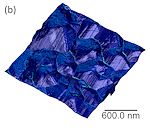 |
Tunnelling AFM (TUNA) images of a the electron emission sites (bright) overlaid with topography for a microcrystalline diamond film. |
 |
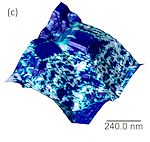
Tunnelling AFM (TUNA) images of a the electron emission sites (bright) overlaid with topography for a nanocrystalline diamond film. |
 |
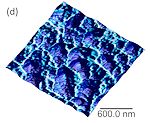
Tunnelling AFM (TUNA) images of a the electron emission sites (bright) overlaid with topography for a P-doped microcrystalline diamond film, showing electron emission is coming from microsteps in the (111) sidewalls and not the square (100) top surface. |
|
 Diamond films on Planar (Flat) Substrates
Diamond films on Planar (Flat) Substrates
























