 Laser Raman Spectroscopy
Laser Raman Spectroscopy
We have a 3-colour laser Raman spectrometer from Renishaw, funded from the EPSRC JREI scheme. This allows the quality of the diamond and DLC (and other films) to be assessed using green (514 nm), UV (325 nm) and IR (785 nm) wavelengths. The machine can also perform line scans, and Raman imaging. Powder and liquid samples can also be analysed, as well as remote samples using a fibre optic link to the microscope. Some images of the system can be seen below. We have recently used this system to obtain Raman spectra for many of the smaller diamondoids.
 |
 |
 |
| Back view of the machine showing the 3 lasers. | Front view of the LRS system. | Front view of the machine. |
 |
 |
|
| Front view with lid open, showing internal optics. | Close up of the internal optics. |
Below are some laser Raman spectra that help characterise diamond films.
 |
 |
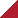
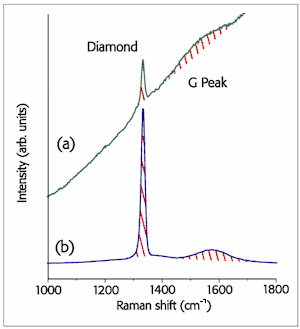
| Raman spectra of microcrystalline CVD diamond taken with (a) 514 nm excitation an (b) 325 nm excitation. The rising background in (b) is due to strong photoluminescence from grain boundaries and nitrogen-vacancy defects. | Raman spectra of microcrystalline CVD diamond grown using a gas mixture of CH4 in H2 with different CH4 mole fractions (%): (a) 0.36, (b) 0.72, (c) 1.08, (d) 1.44 and (e) 2.16. Increasing the CH4 content during growth decreases the quality of the diamond film, as evidenced by the rising G-band around 1550 cm-1. |
 |
|
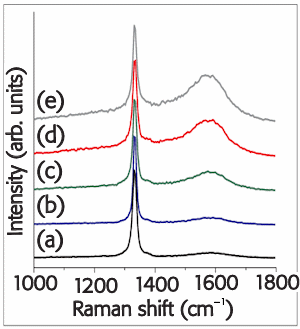
| Raman spectra of a nanocrystalline CVD diamond taken with 325 nm excitation. The peak at 1150 cm-1 come from sp2-carbon species (e.g. trans-polyacetylene) trapped at the numerous grain boundaries. |
Related Papers
- W.N. Wang, N.A. Fox, P.W. May, M.P. Knapper, G. Meaden, P.G. Partridge, M.N.R. Ashfold, J.W. Steeds, L.P. Hayward and G.D. Pitt "Laser Raman Studies of Polycrystalline and Amorphic Diamond Films", Phys. Stat. Sol., 154 (1995) 255.
- S.M. Leeds, T.J. Davis, P.W. May, C.D.O. Pickard and M.N.R. Ashfold, "Use of Different Excitation Wavelengths for the Analysis of CVD Diamond by Laser Raman Spectroscopy", Diamond Relat. Mater. 7 (1998) 233-237.
- J. Filik, P.W. May, S.R.J. Pearce, R.K. Wild, and K.R. Hallam, "XPS and laser Raman analysis of hydrogenated amorphous carbon films", Diamond Relat. Mater. 12 (2003) 974-78.
- G. M. Fuge, P. W. May, K. N. Rosser, S. R. J. Pearce, M. N. R. Ashfold, "Laser Raman and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy of phosphorus containing diamond-like carbon films grown by pulsed laser ablation methods", Diamond Relat. Mater. 13 (2004) 1442-48.
- J. Filik, "Raman Spectroscopy: a simple, non-destructive way to characterise diamond and diamond-like materials", Spectroscopy Europe 17 (2005) 10-17.
- J. Filik, J.N. Harvey, N.L. Allan, P.W. May, J.E.P. Dahl, S. Liu, R.M.K. Carlson, "Raman spectroscopy of nanocrystalline diamond: An ab initio approach", Phys. Rev. B. 74 (2006) 035423 1-10.
- P.W. May, W.J. Ludlow, M. Hannaway, P.J. Heard, J.A. Smith, K.N. Rosser, "Raman and conductivity studies of boron doped microcrystalline diamond, facetted nanocrystalline diamond and cauliflower diamond films", Chem. Phys. Lett. 446 (2007) 103-108.
- P.W. May, P. Overton, J.A. Smith and K.N. Rosser, "Multi-wavelength Raman spectroscopy of nanodiamond particles", Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 1039 (2008) 1039-P15-03.
- P.W. May, J.A. Smith and K.N. Rosser, "785 nm Raman spectroscopy of CVD diamond films", Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 1039 (2008) 1039-P15-02
- P.W. May, W.J. Ludlow, M. Hannaway, P.J. Heard, J.A. Smith, and K.N. Rosser, "Raman and conductivity studies of boron doped microcrystalline diamond, facetted nanocrystalline diamond and cauliflower diamond films", Diamond Relat. Mater. 17 (2008) 105-117.
- P.W. May, J.A. Smith, K.N. Rosser, "785 nm Raman spectroscopy of CVD diamond films", Diamond Relat. Mater. 17 (2008) 199-203.
- S.A. Rahman, M.Z. Othman, P.W. May, "Raman and Photoluminescence Spectroscopy of Nanocrystalline Diamond Films Grown by Hot Filament CVD", Adv. Mater. Res. 501 (2012) 271-275. [doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.501.271]
