Siloxane Resins and Siloxane Resin/Siloxane Polymer Blends

Natalie Benton (previous student, left the group in 2004)
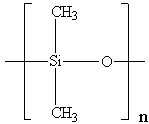
This project involves using NMR relaxation and diffusion experiments as well as small-angle neutron and x-ray scattering techniques to elucidate the interaction between MQ resins and siloxane-based polymers.
The aim of the project is to achieve more efficient control of the physical and chemical properties of resins which function to reinforce and modify the viscoelastic properties of polydimethylsiloxane. It is hoped that tools will be developed to better understand resin structures and the structural features responsible for the energy dissipating characteristics that contribute to toughness.
The objective of NMR and SANS experiments is to determine the primary factors (such as the size and shape of resins and polymer size) that impact polymer mobility and resin interaction.
Experimental work will focus on:
- The critical polymer size at which entanglement reduction is induced by a typical MQ resin
- The critical resin size that delineates between reinforcement/hydrodynamic and solvation/entanglement effects
The techniques used and findings from model systems will be applied to commercial Dow Corning products including pressure-sensitive adhesives and antifoams.
References
NMR Spin-Relaxation Studies of Reinforced Polydimethylsiloxane Melts; T. Cosgrove, M. Turner, I. Weatherhead, C. Roberts, T. Garasanin, R. Schmidt, G. Gordon, J. Hannington; ACS Symposium Series, 2000, 729, 204
Diffusion of Polydimethylsiloxane Mixtures with Polysilicate Nanoparticles; C. Roberts, T. Cosgrove, G. Gordon, R. Schmidt; Macromolecules, 2001, 34, 538
This project is funded by the EPSRC and Dow Corning