

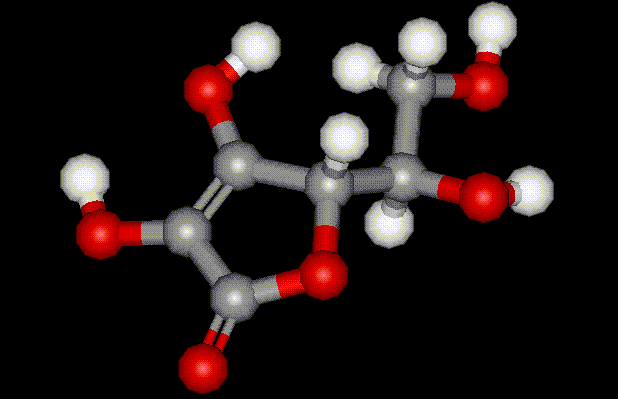
 The body stores little ascorbic acid or vitamin C, so this must be provided on a daily basis in the diet. Good sources of vitamin C include citrus fruit, raw cabbage, strawberries and tomatoes. Vitamin C has been shown to prevent scurvy, and is essential for healthy blood vessels, bones, and teeth. Vitamin C also helps form collagen, a protein that holds tissues together. Ascorbic acid is industrially synthesised using a number of different biological techniques, and is used as a flour improving agent, a browning inhibitor in fresh produce, and an antioxidant in beers.
The body stores little ascorbic acid or vitamin C, so this must be provided on a daily basis in the diet. Good sources of vitamin C include citrus fruit, raw cabbage, strawberries and tomatoes. Vitamin C has been shown to prevent scurvy, and is essential for healthy blood vessels, bones, and teeth. Vitamin C also helps form collagen, a protein that holds tissues together. Ascorbic acid is industrially synthesised using a number of different biological techniques, and is used as a flour improving agent, a browning inhibitor in fresh produce, and an antioxidant in beers.
| Other names: | l-ascorbic acid, l,3-ketothreohexuronic acid |
| Molecular formula: | C6 H8 O6 |
| CAS No: | 50-81-7 |
| Physical appearance: | white crystals or powder |
| Melting point: | 193 (dec.) |
| Other information: | May be harmful if ingested in quantity. May act as an irritant. |
| Other names: | ascorbic acid sodium salt, ascorbicin, ascorbin, cebitate, cenolate, monosodium ascorbate |
| CAS No: | 134-03-2 |
| Physical appearance: | white to off-white solid |
| Melting point: | 220 C (dec.) |
| Other information: | No adverse health effects. |
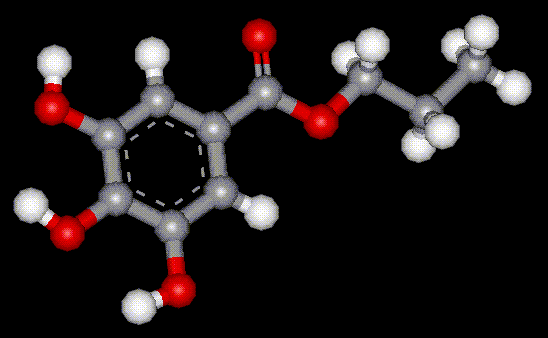 Propyl gallate is synthesised by the esterification of gallic acid. It is used as an antioxidant in food, often with BHT (E321) and BHA (E320), although it has limited use as it is unstable at high temperatures.
Propyl gallate is synthesised by the esterification of gallic acid. It is used as an antioxidant in food, often with BHT (E321) and BHA (E320), although it has limited use as it is unstable at high temperatures.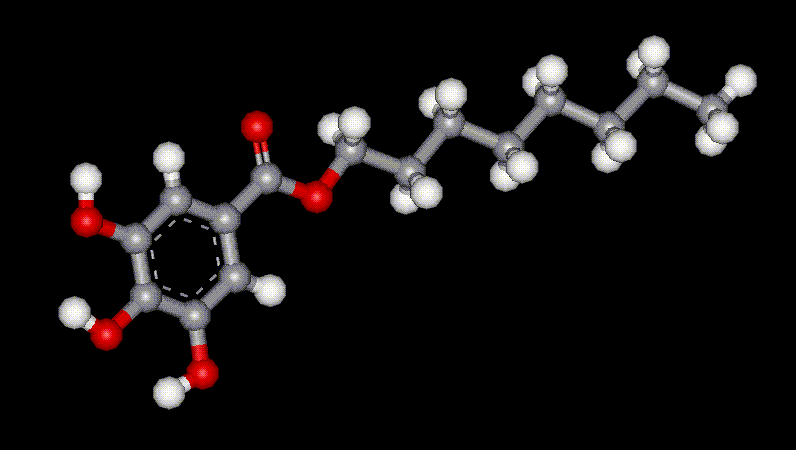 Octyl gallate is synthesised by the esterification of gallic acid. It is used as an antioxidant in food, often with BHT (E321) and BHA (E320), although it has limited use as it is unstable at high temperatures.
Octyl gallate is synthesised by the esterification of gallic acid. It is used as an antioxidant in food, often with BHT (E321) and BHA (E320), although it has limited use as it is unstable at high temperatures.| Other names: | araboascorbic acid, d-isoascorbic acid, glucosaccharonic acid, erycorbin, saccharosonic acid |
| Molecular formula: | C6H8O6 |
| CAS No: | 89-65-6 |
| Physical appearance: | solid |
| Melting point: | 169 - 172 C (decomposes) |
| Other information: | Eye, skin and respiratory irritant. |
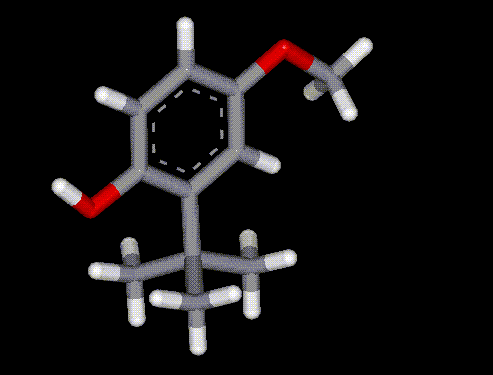 BHA is a synthetic analogue of vitamin E and operates by reducing oxygen radicals and interrupting the propagation of oxidation processes. It is widely used as an antioxidant and preservative, and is prepared from p-methoxyphenol and isobutene. BHA can be used in baked products as it is stable at high temperatures, it is mainly used to prevent rancidity in fats and oils.
BHA is a synthetic analogue of vitamin E and operates by reducing oxygen radicals and interrupting the propagation of oxidation processes. It is widely used as an antioxidant and preservative, and is prepared from p-methoxyphenol and isobutene. BHA can be used in baked products as it is stable at high temperatures, it is mainly used to prevent rancidity in fats and oils.| Other names: | tert-butyl-4-hydroxyanisole, tert-butyl-4-methoxyphenol, BOA, (1,1-dimethylethyl)-4-methoxyphenol |
| Molecular formula: | C11 H16 O2 |
| CAS No: | 25013-16-5 |
| Physical appearance: | white or light yellow waxy solid with an aromatic odour |
| Melting point: | 48 C |
| Boiling point: | 264 C |
| Other information: | Possible human carcinogen; apparently carcinogenic in animal experiments. May be harmful by ingestion or inhalation. May act as a skin, eye or respiratory irritant. |
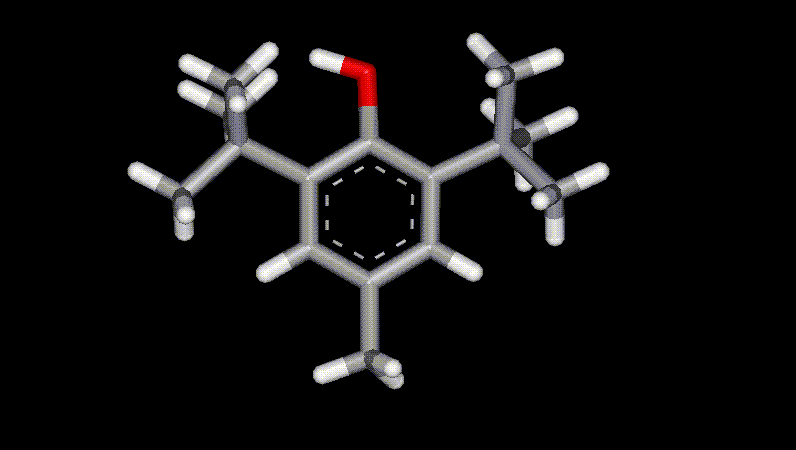 BHT is a synthetic analogue of vitamin E and operates by reducing oxygen radicals and interrupting the propagation of oxidation processes. It is widely used as an antioxidant and preservative, and is prepared from p-cresol and isobutylene. It is one of the most commonly used antioxidants for food oils and fats and is much cheaper than BHA although it has more limited applications due to instability at high temperatures. There is evidence that BHT causes cell division.
BHT is a synthetic analogue of vitamin E and operates by reducing oxygen radicals and interrupting the propagation of oxidation processes. It is widely used as an antioxidant and preservative, and is prepared from p-cresol and isobutylene. It is one of the most commonly used antioxidants for food oils and fats and is much cheaper than BHA although it has more limited applications due to instability at high temperatures. There is evidence that BHT causes cell division.| Other names: | 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol, 2,6-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)-4-methylphenol |
| Molecular formula: | C15H24O |
| CAS No: | 128-37-0 |
| Physical appearance: | white crystalline solid |
| Melting point: | 71 C |
| Boiling point: | 265 C |
| Other information: | Cancer suspect agent. May cause reproductive defects. May be harmful if swallowed. Eye, respiratory tract and skin irritant. |
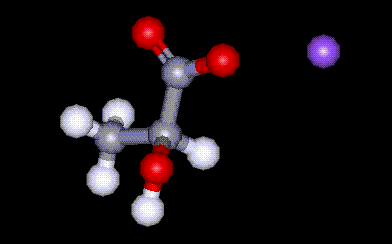 Sodium lactate is the sodium salt of lactic acid, E270, and is used as a humectant and antioxidant in food. It is capable of increasing the antioxidant effects of other substances. It is hygroscopic hence is used in such products where its ability to absorb moisture helps to extend shelf life. Sometimes used as a substitute for glycerol.
Sodium lactate is the sodium salt of lactic acid, E270, and is used as a humectant and antioxidant in food. It is capable of increasing the antioxidant effects of other substances. It is hygroscopic hence is used in such products where its ability to absorb moisture helps to extend shelf life. Sometimes used as a substitute for glycerol.| Other names: | lacolin, lactic acid sodium salt |
| Molecular formula: | C3 H5 O3 Na |
| CAS No: | 72-17-3 |
| Physical appearance: | colourless liquid |
| Melting point: | 17 C |
| Boiling point: | 113 C |
| Other information: | Not believed to present a health risk. |
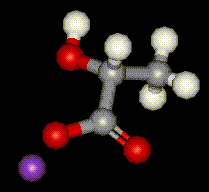 Potassium lactate is hygroscopic, hence is used in foods where it is used to help retain moisture. It is used in meat and poultry to control food-borne pathogenic bacteria and to protect and enhance meat flavour.
Potassium lactate is hygroscopic, hence is used in foods where it is used to help retain moisture. It is used in meat and poultry to control food-borne pathogenic bacteria and to protect and enhance meat flavour.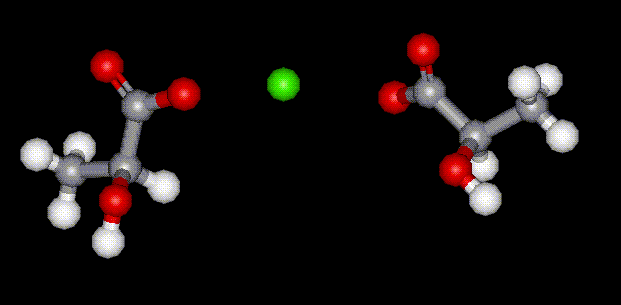 Calcium lactate is the calcium salt of lactic acid, E270, and is used as a humectant and antioxidant in food. It is capable of increasing the antioxidant effects of other substances. It is hygroscopic hence is used in such products where its ability to absorb moisture helps to extend shelf life. Sometimes used as a substitute for glycerol.
Calcium lactate is the calcium salt of lactic acid, E270, and is used as a humectant and antioxidant in food. It is capable of increasing the antioxidant effects of other substances. It is hygroscopic hence is used in such products where its ability to absorb moisture helps to extend shelf life. Sometimes used as a substitute for glycerol.| Other names: | calcium lactate 5-hydrate, calcium lactate, 2-hydroxypropanoic acid calcium salt pentahydrate |
| Molecular formula: | (CH3CHOHCOO)2 Ca . 5H2O |
| CAS No: | 63690-56-2 |
| Physical appearance: | white crystalline powder |
| Other information: | Not believed to present a significant health risk. |
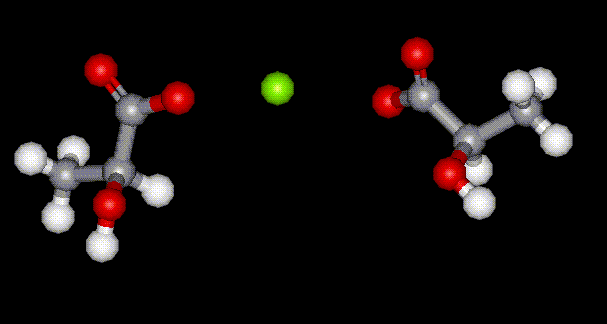 Magnesium lactate is the magnesium salt of lactic acid, E270, and is used as a humectant and antioxidant in food. It is capable of increasing the antioxidant effects of other substances. It is hygroscopic hence is used in such products where its ability to absorb moisture helps to extend shelf life. Sometimes used as a substitute for glycerol.
Magnesium lactate is the magnesium salt of lactic acid, E270, and is used as a humectant and antioxidant in food. It is capable of increasing the antioxidant effects of other substances. It is hygroscopic hence is used in such products where its ability to absorb moisture helps to extend shelf life. Sometimes used as a substitute for glycerol.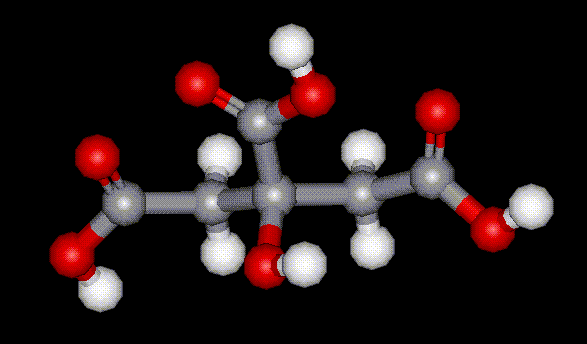 Citric acid is a vital component of the citric acid cycle, or Krebs cycle. During this sequence of reactions one acetate unit is converted to two equivalents of carbon dioxide giving rise to a molecule of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the main energy source in cells. Citric acid occurs abundantly in citrus fruits, although commercial synthesis is by fermentation of molasses. It is used in food as an antioxidant as well as enhancing the effect of other antioxidants, and also as an acidity regulator. Present in virtually all plants, it was first isolated in 1784 from lemon juice, by the Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele, and has been used as a food additive for over 100 years.
Citric acid is a vital component of the citric acid cycle, or Krebs cycle. During this sequence of reactions one acetate unit is converted to two equivalents of carbon dioxide giving rise to a molecule of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the main energy source in cells. Citric acid occurs abundantly in citrus fruits, although commercial synthesis is by fermentation of molasses. It is used in food as an antioxidant as well as enhancing the effect of other antioxidants, and also as an acidity regulator. Present in virtually all plants, it was first isolated in 1784 from lemon juice, by the Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele, and has been used as a food additive for over 100 years. | Other names: | citric acid, anhydrous |
| Molecular formula: | HOC(COOH)(CH2COOH)2 |
| CAS No: | 77-92-9 |
| Physical appearance: | colourless, odourless translucent powder |
| Melting point: | 153 C |
| Other information: | may cause irritation to the respiratory tract |
| Other names: | 2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylic acid trisodium salt |
| Molecular formula: | C6H8O7Na3 |
| CAS No: | 6132-04-3 |
| Physical appearance: | white powder or colourless crystals |
| Melting point: | 300 C |
| Other information: | May act as an irritant or be harmful. |
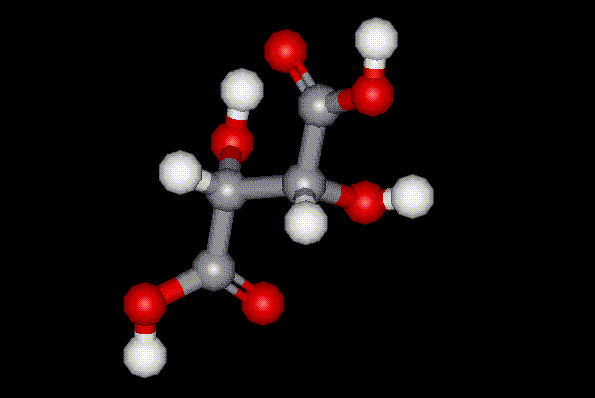 Tartaric acid exists as a pair of enantiomers and an achiral meso compound. (+)-tartaric acid
Tartaric acid exists as a pair of enantiomers and an achiral meso compound. (+)-tartaric acid  commonly occurs in nature and can be found in fruit, and sometimes in wine. Tartaric acid is industrially synthesised as a byproduct during wine making, and it is used in food as an antioxidant and synergist to increase the antioxidant effect of other substances. It is also used as an acidity regulator and sequestrant. Excessive ingestion of tartaric acid results in laxative effects.
commonly occurs in nature and can be found in fruit, and sometimes in wine. Tartaric acid is industrially synthesised as a byproduct during wine making, and it is used in food as an antioxidant and synergist to increase the antioxidant effect of other substances. It is also used as an acidity regulator and sequestrant. Excessive ingestion of tartaric acid results in laxative effects.| Molecular formula: | C4H6O6 |
| CAS No: | 147-71-7 |
| Physical appearance: | white crystals |
| Melting point: | 172 - 174 C |
| Boiling point: | 275 C |
| Other information: | May be harmful by inhalation, ingestion or skin absorption. May act as an irritant. |
| Molecular formula: | C4 H6 O6 Na2 |
| CAS No: | 6106-24-7 |
| Physical appearance: | white crystalline powder |
| Other information: | May be harmful. May act as an irritant. |
| Other names: | orthophosphoric acid |
| Molecular formula: | H3PO4 |
| CAS No: | 7664-38-2 |
| Physical appearance: | colourless odourless liquid |
| Melting point: | 21 C (pure) |
| Boiling point: | 158 C (pure) |
| Other information: | Corrosive - causes burns. Harmful if swallowed and in contact with skin. May be harmful through inhalation. Very destructive of mucous membranes, respiratory tract, eyes and skin. |
| Other names: | Sodium biphosphate, sodium dihydrogen phosphate |
| Molecular formula: | NaH2PO4 |
| CAS No: | 7558-80-7 |
| Physical appearance: | white, odourless, crystalline powder |
| Other information: | May be a skin, respiratory and eye irritant, may cause internal burns when ingested in excess. |
| Other names: | disodium hydrogen phosphate, disodium orthophosphate, sodium hydrogen phosphate, disodium monohydrogen phosphate, phosphoric acid disodium salt |
| Molecular formula: | HNa2PO4 |
| CAS No: | 7558-79-4 |
| Physical appearance: | white granular powder |
| Other information: | Eye and skin irritant. May be harmful if ingested in quantity. |
| Other names: | dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, dipotassium hydrogen orthophosphate, phosphoric acid dipotassium salt, potassium hydrogen phosphate |
| Molecular formula: | K2 H PO4 |
| CAS No: | 7758-11-4 |
| Physical appearance: | white powder or crystals |
| Other information: | May cause eye or skin irritation. |
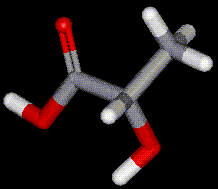 Lactic acid is a naturally occurring compound present in sour milk, molasses and fruit. Lactic acid is produced commercially by fermentation of carbohydrates in the presence of lactic acid bacteria. Lactic acid occurs naturally in the blood (lactates) when glycogen is broken down in the muscles.
Lactic acid is a naturally occurring compound present in sour milk, molasses and fruit. Lactic acid is produced commercially by fermentation of carbohydrates in the presence of lactic acid bacteria. Lactic acid occurs naturally in the blood (lactates) when glycogen is broken down in the muscles.