

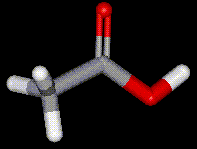
 Acetic acid (ethanoic acid) has been used for hundreds of years
Acetic acid (ethanoic acid) has been used for hundreds of years  as a preservative (vinegar, French for "sour wine"). If during the fermentation of grapes or other
fruits, oxygen is allowed into the container, then bacteria convert the ethanol present into ethanoic acid causing the wine to turn sour. Acetic acid may be synthetically produced using methanol carbonylation, acetaldehyde oxidation, or butane/naphtha oxidation. Pure acetic acid is termed "glacial", and is completely miscible with water.
as a preservative (vinegar, French for "sour wine"). If during the fermentation of grapes or other
fruits, oxygen is allowed into the container, then bacteria convert the ethanol present into ethanoic acid causing the wine to turn sour. Acetic acid may be synthetically produced using methanol carbonylation, acetaldehyde oxidation, or butane/naphtha oxidation. Pure acetic acid is termed "glacial", and is completely miscible with water.| Other names: | ethanoic acid |
| Molecular formula: | C2 H4 O2 |
| CAS No: | 64-19-7 |
| Melting point: | 16.7 C |
| Boiling point: | 118 C |
| Other information: | Acetic acid is strongly corrosive and causes serious burns, as well as being a lachrymator. |

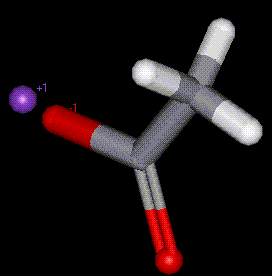 The potassium salt of acetic acid, E260. In industry is used to aid conditioning of fabrics, used in the manufacture of penicillin.
The potassium salt of acetic acid, E260. In industry is used to aid conditioning of fabrics, used in the manufacture of penicillin.
| Other names: | acetic acid potassium salt, potassium ethanoate, ethanoic acid potassium salt |
| Molecular formula: | CH3COOK |
| CAS No: | 127-08-2 |
| Melting point: | 292 C |
| Other information: | May irritate the skin, eyes and lungs. |
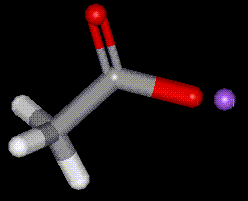 The sodium salt of acetic acid, E260. Acts as a buffer in foods. Technical grade sodium acetate is used as a mordant in dyeing processes, as buffers in petroleum production, and for kidney dialysis processes. In plastic manufacturing it is used as a retarder for some elastomers.
The sodium salt of acetic acid, E260. Acts as a buffer in foods. Technical grade sodium acetate is used as a mordant in dyeing processes, as buffers in petroleum production, and for kidney dialysis processes. In plastic manufacturing it is used as a retarder for some elastomers.| Other names: | sodium acetate (anhydrous) |
| Molecular formula: | CH3COONa |
| CAS No: | 127-09-3 |
| Physical appearance: | white crystalline powder |
| Melting point: | 324 C |
| Other information: | May irritate the skin, harmful if ingested |
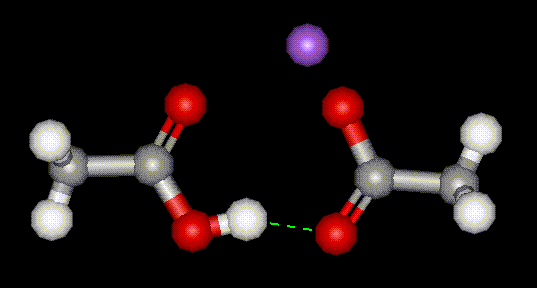 A vinegar used as a mould inhibitor in snack foods and bread, as a flavour enhancer in breads, cakes, cheese and snack food. Technical grade sodium hydrogen acetate is used as a buffer in petroleum production.
A vinegar used as a mould inhibitor in snack foods and bread, as a flavour enhancer in breads, cakes, cheese and snack food. Technical grade sodium hydrogen acetate is used as a buffer in petroleum production.| CAS No: | 126-96-5 |
| Chemical formula: | C4H7O4Na |
| Other information: | a compound of acetic acid and sodium acetate |
 Calcium acetate is used in food as a thickening agent (cake mixtures, puddings, pie fillings), as a buffer in controlling the pH of food during processing, as a preservative to prevent microbial growth, and as a calcium supplement in pet products. In other areas of industry calcium acetate is used in dyeing and printing.
Calcium acetate is used in food as a thickening agent (cake mixtures, puddings, pie fillings), as a buffer in controlling the pH of food during processing, as a preservative to prevent microbial growth, and as a calcium supplement in pet products. In other areas of industry calcium acetate is used in dyeing and printing.| Other names: | calcium acetate monohydrate, calcium diacetate |
| Molecular formula: | Ca C4 H6 O4 |
| CAS No: | 5743-26-0 or 62-54-4 |
| Physical appearance: | white crystals or powder |
| Other information: | May cause eye, skin or respiratory irritation. Mutagenic effects noted in laboratory tests. |
 A gas present in air, produced in combustion, fermentation and animal metabolism. Carbon dioxide is produced when any form of carbon or almost any carbon compound is burned in an excess of oxygen. In animal respiration carbon dioxide combines with haemoglobin in red blood cells, is carried to the lungs and is breathed out. Green vegetation uses chlorophyll to combine carbon dioxide with hydrogen to form carbohydrates (photosynthesis).
A gas present in air, produced in combustion, fermentation and animal metabolism. Carbon dioxide is produced when any form of carbon or almost any carbon compound is burned in an excess of oxygen. In animal respiration carbon dioxide combines with haemoglobin in red blood cells, is carried to the lungs and is breathed out. Green vegetation uses chlorophyll to combine carbon dioxide with hydrogen to form carbohydrates (photosynthesis). | Other names: | carbonic anhydride, dry ice |
| Molecular formula: | CO2 |
| CAS No: | 124-38-9 |
| Physical appearance: | colourless odourless gas |
| Boiling point: | -78 C (sublimes) |
| Other information: | acts as an asphyxiant in high concentration. Can cause cold burns when solid. |
 Occurs in two chiral molecules, the D- and L- forms. L-malic acid is a naturally occurring organic acid that is used in the body to derive ATP from food (see the citric acid cycle). It is found in many fruits and vegetables, especially apples. Malic acid may aid in the treatment of fibromyalgia. Commercial malic acid is usually a mixture of the two types, synthesised by heating maleic acid with dilute sulphuric acid, under pressure.
Occurs in two chiral molecules, the D- and L- forms. L-malic acid is a naturally occurring organic acid that is used in the body to derive ATP from food (see the citric acid cycle). It is found in many fruits and vegetables, especially apples. Malic acid may aid in the treatment of fibromyalgia. Commercial malic acid is usually a mixture of the two types, synthesised by heating maleic acid with dilute sulphuric acid, under pressure.| Other names: | DL-Malic acid, hydroxybutanedioic acid |
| Molecular formula: | HOCOCH2CHOHCOOH |
| CAS No: | 617-48-1 |
| Physical appearance: | Odourless white crystals |
| Melting point: | 130 C |
| Boiling point: | 150 C |
| Other information: | Irritant, harmful if swallowed, inhaled or absorbed through skin. |
 Fumaric acid is a geometric isomer of maleic acid, and can be prepared from maleic acid by heating, as well as by catalytic oxidation of benzene or by bacterial action on glucose. Essential in respiration of animal and plant tissue, used in the Kreb's cycle. Added to foods as an acidity regulator and flavouring agent, may be used as a substitute for cream of tartar. It is used as a mordant in dyeing and in the manufacture of synthetic resins and polyhydric alcohols.
Fumaric acid is a geometric isomer of maleic acid, and can be prepared from maleic acid by heating, as well as by catalytic oxidation of benzene or by bacterial action on glucose. Essential in respiration of animal and plant tissue, used in the Kreb's cycle. Added to foods as an acidity regulator and flavouring agent, may be used as a substitute for cream of tartar. It is used as a mordant in dyeing and in the manufacture of synthetic resins and polyhydric alcohols.| Other names: | 2-butenedioic acid, trans-butenedioic acid, butenedioic acid |
| Molecular formula: | C4H4O4 |
| CAS No: | 110-17-8 |
| Physical appearance: | white powder or colourless crystals |
| Melting point: | 299 C |
| Other information: | May irritate the eyes or respiratory tract. |
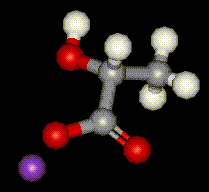 Potassium lactate is hygroscopic, hence is used in foods where it is used to help retain moisture. It is used in meat and poultry to control food-borne pathogenic bacteria and to protect and enhance meat flavour.
Potassium lactate is hygroscopic, hence is used in foods where it is used to help retain moisture. It is used in meat and poultry to control food-borne pathogenic bacteria and to protect and enhance meat flavour.| Other names: | 1,2,3-Propanetricarboxylic acid, 2-hydroxy-, Tricalcium citrate |
| Molecular formula: | C12H10Ca3O14 |
| CAS No: | 813-94-5 |
| Physical appearance: | white powder or white to colourless crystals |
| Other information: | low toxicity |
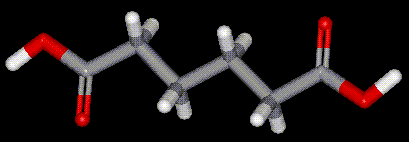 Adipic acid occurs naturally in living cells, but is commercially prepared from the oxidation of cyclohexanol by concentrated nitric acid.
Adipic acid occurs naturally in living cells, but is commercially prepared from the oxidation of cyclohexanol by concentrated nitric acid.| Other names: | hexanedioic acid, 1,4-butanedicarboxylic acid |
| Molecular formula: | HOCO(CH2)4COOH |
| CAS No: | 124-04-9 |
| Physical appearance: | white crystalline powder |
| Melting point: | 152 C |
| Boiling point: | 337 C |
| Other information: | Inhalation may cause irritation. |
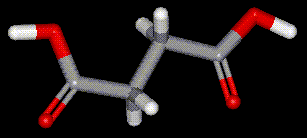 Succinic acid occurs naturally in fossils, fungi and lichen, and is commercially prepared from acetic acid.
Succinic acid occurs naturally in fossils, fungi and lichen, and is commercially prepared from acetic acid.| Other names: | butanedionic acid, amber acid |
| Molecular formula: | HOOCCH2CH2COOH |
| CAS No: | 110-15-6 |
| Physical appearance: | Colourless odourless prisms |
| Melting point: | 185 C |
| Boiling point: | 235 C |
| Other information: | Corrosive, causes burns. Harmful by inhalation, ingestion and through skin absorption. |
| Other names: | ferric ammonium citrate, ammonium ferric citrate, iron ammonium citrate |
| CAS No: | 1185-57-5 |
| Physical appearance: | brown or green powder or crystals |
| Other information: | May decompose upon exposure to light, may irritate the eyes, skin and respiratory tract. |
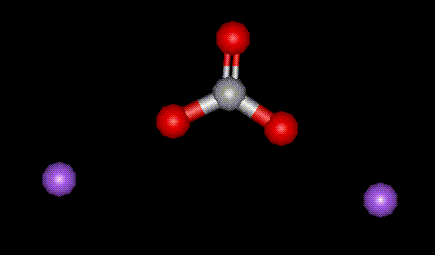 Sodium carbonate is naturally occurring in alkaline waters, however it is also synthesised by the Solvay process or by electrolysis of sea water. Sodium carbonate is used as an acidity regulator, particularly in beer making. Excessive ingestion may result in stomach upset.
Sodium carbonate is naturally occurring in alkaline waters, however it is also synthesised by the Solvay process or by electrolysis of sea water. Sodium carbonate is used as an acidity regulator, particularly in beer making. Excessive ingestion may result in stomach upset.| Other names: | sodium carbonate, soda ash, disodium carbonate |
| Molecular formula: | Na2 CO3 |
| CAS No: | 497-19-8 |
| Physical appearance: | white odourless powder |
| Melting point: | 851 C |
| Other information: | May irritate the eyes and respiratory tract. |
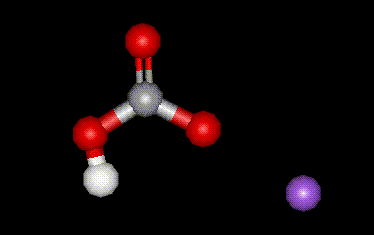 Sodium hydrogen carbonate is used in food mainly as a raising agent, but also as a base. It is prepared synthetically.
Sodium hydrogen carbonate is used in food mainly as a raising agent, but also as a base. It is prepared synthetically.| Other names: | bicarbonate of soda, baking soda, sodium hydrogen carbonate |
| Molecular formula: | NaHCO3 |
| CAS No: | 144-55-8 |
| Physical appearance: | white powder or crystals |
| Melting point: | 50 C |
| Other information: | May irritate the eyes |
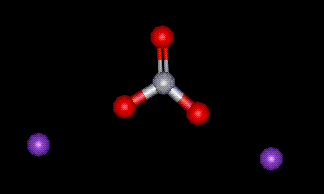 Potassium carbonate is used purely as a base in foods to regulate pH. There are no known adverse health effects.
Potassium carbonate is used purely as a base in foods to regulate pH. There are no known adverse health effects.| Other names: | Potassium Carbonate, anhydrous |
| Molecular formula: | K2CO3 |
| CAS No: | 584-08-7 |
| Physical appearance: | white, odourless powder |
| Melting point: | 891 C |
| Other information: | may irritate the eyes, skin and lungs if inhaled |
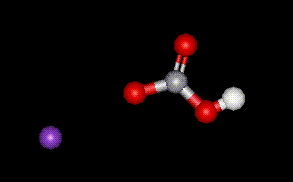 Potassium hydrogen carbonate is used purely as a base in foods to regulate pH. There are no known adverse health effects.
Potassium hydrogen carbonate is used purely as a base in foods to regulate pH. There are no known adverse health effects.| Other names: | potassium acid carbonate |
| Molecular formula: | K H C O3 |
| CAS No: | 298-14-6 |
| Physical appearance: | white powder or crystals |
| Melting point: | 100 C |
| Other information: | dust may irritate the eyes or respiratory system |
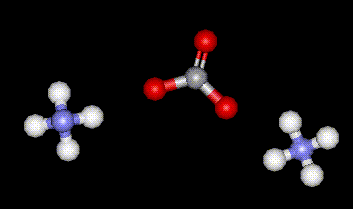 Ammonium carbonate is obtained by subliming a mixture of ammonium sulphate and calcium carbonate. It is used as a buffer in food, there may be some adverse health effects due to over-consumption as ammonium carbonate is converted into carbon dioxide in the stomach.
Ammonium carbonate is obtained by subliming a mixture of ammonium sulphate and calcium carbonate. It is used as a buffer in food, there may be some adverse health effects due to over-consumption as ammonium carbonate is converted into carbon dioxide in the stomach.| Other names: | diammonium carbonate, carbonic acid ammonium salt |
| Molecular formula: | (NH4)2CO3 |
| CAS No: | 506-87-6 |
| Physical appearance: | white powder |
| Other information: | Eye, skin and respiratory irritant. May be harmful if inhaled. |
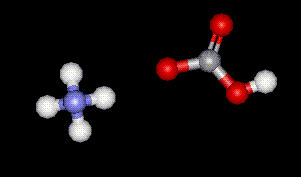 Ammonium hydrogen carbonate is synthesised by passing carbon dioxide through ammonia solution. It is used as a buffer in food, as well as a raising agent.
Ammonium hydrogen carbonate is synthesised by passing carbon dioxide through ammonia solution. It is used as a buffer in food, as well as a raising agent.| Other names: | Ammonium bicarbonate |
| Molecular formula: | NH4HCO3 |
| CAS No: | 1066-33-7 |
| Physical appearance: | colourless to white crystals with an ammonia odour |
| Other information: | Eye, skin and respiratory irritant. May be harmful if inhaled |
 Magnesium carbonate is used mainly as a buffer and anti-caking agent, but it is also used as an anti-bleaching agent.
Magnesium carbonate is used mainly as a buffer and anti-caking agent, but it is also used as an anti-bleaching agent.| Other names: | magnesium carbonate, magnesium (II) carbonate n-hydrate |
| Molecular formula: | MgCO3 nH2O |
| CAS No: | 23389-33-5 |
| Physical appearance: | white powder |
| Other information: | May act as a skin, eye or respiratory irritant. |
 Potassium chloride is abundant in saline rock residues, and in food can be used as a gelling agent as well as an acidity regulator.
Potassium chloride is abundant in saline rock residues, and in food can be used as a gelling agent as well as an acidity regulator.| Other names: | potassium muriate |
| Molecular formula: | KCl |
| CAS No: | 7447-40-7 |
| Physical appearance: | white crystals or powder |
| Melting point: | 776 C |
| Boiling point: | sublimes at 1500 C |
| Other information: | low toxicity, although ingestion of large quantities may be harmful. |
| Molecular formula: | CaCl2 |
| CAS No: | 10043-52-4 |
| Physical appearance: | white granules, pellets or powder |
| Melting point: | 772 C |
| Other information: | Irritant,may cause burns. Harmful if swallowed. |
| Other names: | sal ammoniac, ammonium muriate |
| Molecular formula: | NH4Cl |
| CAS No: | 12125-02-9 |
| Physical appearance: | white crystalline powder |
| Melting point: | 340 C (sublimes) |
| Other information: | Harmful if swallowed. May be harmful by inhalation. Skin, eye and respiratory irritant |
| Other names: | magnesium (II) chloride |
| Molecular formula: | Mg Cl2 |
| CAS No: | 7786-30-3 |
| Physical appearance: | white powder |
| Melting point: | 714C |
| Other information: | Eye and skin irritant. |
| Other names: | Tin(II)chloride, tin dichloride, tin dihydrate |
| Molecular formula: | SNCL2 2H2O |
| CAS No: | 10025-69-1 |
| Physical appearance: | white odourless powder |
| Melting point: | 37 C |
| Other information: | may be carcinogenic |
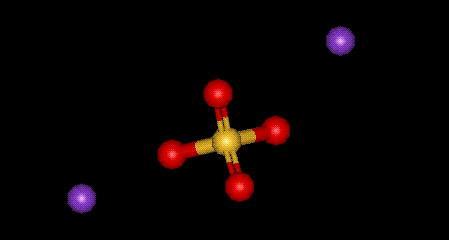
| Other names: | disodium sulfate |
| Molecular formula: | Na2 SO4 |
| CAS No: | 7757-82-6 |
| Physical appearance: | White crystals or powder |
| Melting point: | 884 |
| Other information: | Hygroscopic, may be harmful if swallowed. |
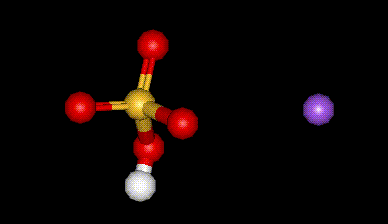
| Other names: | sodium hydrogen sulphate, sodium bisulfate, sodium bisulphate, sodium pyrosulphate, sodium pyrosulfate, sulfuric acid monosodium salt |
| Molecular formula: | H Na SO4 H2O |
| CAS No: | 7681-38-1 |
| Physical appearance: | off-white granules, crystals or powder |
| Melting point: | 59 C |
| Other information: | Harmful if swallowed, inhaled or in contact with skin. Corrosive,causes burns. Very destructive of mucous membranes. |
| Molecular formula: | K2SO4 |
| CAS No: | 7778-80-5 |
| Physical appearance: | white powder |
| Melting point: | 1067 C |
| Boiling point: | 1670 C |
| Other information: | skin and eye irritant |
 Calcium sulphate occurs naturally in the form of gypsum, and may be used as a sequestrant in food as well as a buffer and firming agent.
Calcium sulphate occurs naturally in the form of gypsum, and may be used as a sequestrant in food as well as a buffer and firming agent.| Other names: | Anhydrous gypsum |
| Molecular formula: | CaSO4 |
| CAS No: | 7778-18-9 |
| Physical appearance: | white odourless powder |
| Melting point: | 1450 C |
| Other information: | may irritate nose and eyes |